Treatment of accommodative dysfunction in children: results from a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 21873922
- PMCID: PMC3204163
- DOI: 10.1097/OPX.0b013e31822f4d7c
Treatment of accommodative dysfunction in children: results from a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Purpose: To report the effectiveness of various forms of vision therapy/orthoptics in improving accommodative amplitude and facility in children with symptomatic convergence insufficiency (CI) and co-existing accommodative dysfunction.
Methods: In a randomized clinical trial, 221 children aged 9 to 17 years with symptomatic CI were assigned to one of four treatments. Of the enrolled children, 164 (74%) had accommodative dysfunction; 63 (29%) had a decreased amplitude of accommodation with respect to age, 43 (19%) had decreased accommodative facility, and 58 (26%) had both. Analysis of variance models were used to compare mean accommodative amplitude and accommodative facility for each treatment group after 4, 8, and 12 weeks of treatment.
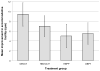
Results: After 12 weeks of treatment, the increases in amplitude of accommodation [office-based vergence/accommodative therapy with home reinforcement group (OBVAT) 9.9 D, home-based computer vergence/accommodative therapy group (HBCVAT+) 6.7 D, and home-based pencil push-up therapy group (HBPP) 5.8 D] were significantly greater than in the office-based placebo therapy (OBPT) group (2.2 D) (p-values ≤0.010). Significant increases in accommodative facility were found in all groups (OBVAT: 9 cpm, HBCVAT+: 7 cpm, HBPP: 5 cpm, OBPT: 5.5 cpm); only the improvement in the OBVAT group was significantly greater than that found in the OBPT group (p = 0.016). One year after completion of therapy, reoccurrence of decreased accommodative amplitude was present in only 12.5% and accommodative facility in only 11%.
Conclusions: Vision therapy/orthoptics is effective in improving accommodative amplitude and accommodative facility in school-aged children with symptomatic CI and accommodative dysfunction.
Figures



References
-
- Scheiman M, Gallaway M, Coulter R, Reinstein F, Ciner E, Herzberg C, Parisi M. Prevalence of vision and ocular disease conditions in a clinical pediatric population. J Am Optom Assoc. 1996;67:193–202. - PubMed
-
- Borsting E, Rouse MW, Deland P. Evaluation of symptoms in school-aged children with accommodative insufficiency. Optom Vis Sci. 1999;76(Suppl):205.
-
- Abrams D. Duke-Elder’s Practice of Refraction. 10. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone; 1993.
-
- Rouse MW. Management of binocular anomalies: efficacy of vision therapy in the treatment of accommodative deficiencies. Am J Optom Physiol Opt. 1987;64:415–20. - PubMed
-
- Scheiman M, Wick B. Clinical Management of Binocular Vision: Heterophoric, Accommodative and Eye Movement Disorders. 3. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins; 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

