Dynamic maintenance of asymmetric meiotic spindle position through Arp2/3-complex-driven cytoplasmic streaming in mouse oocytes
- PMID: 21874009
- PMCID: PMC3523671
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb2320
Dynamic maintenance of asymmetric meiotic spindle position through Arp2/3-complex-driven cytoplasmic streaming in mouse oocytes
Abstract
Mature mammalian oocytes are poised for completing meiosis II (MII) on fertilization by positioning the spindle close to an actomyosin-rich cortical cap. Here, we show that the Arp2/3 complex localizes to the cortical cap in a Ran-GTPase-dependent manner and nucleates actin filaments in the cortical cap and a cytoplasmic actin network. Inhibition of Arp2/3 activity leads to rapid dissociation of the spindle from the cortex. Live-cell imaging and spatiotemporal image correlation spectroscopy analysis reveal that actin filaments flow continuously away from the Arp2/3-rich cortex, driving a cytoplasmic streaming expected to exert a net pushing force on the spindle towards the cortex. Arp2/3 inhibition not only diminishes this actin flow and cytoplasmic streaming but also enables a reverse streaming driven by myosin-II-based cortical contraction, moving the spindle away from the cortex. Thus, the asymmetric MII spindle position is dynamically maintained as a result of balanced forces governed by the Arp2/3 complex.
Figures
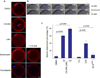
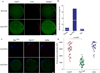
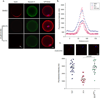
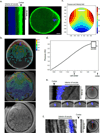
Comment in
-
Spindle positioning: going against the actin flow.Nat Cell Biol. 2011 Oct 3;13(10):1183-5. doi: 10.1038/ncb2352. Nat Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21968992
References
-
- Sathananthan AH. Ultrastructure of the human egg. Hum Cell. 1997;10:21–38. - PubMed
-
- Webb M, Howlett SK, Maro B. Parthenogenesis and cytoskeletal organization in ageing mouse eggs. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1986;95:131–145. - PubMed
-
- Kim NH, Moon SJ, Prather RS, Day BN. Cytoskeletal alteration in aged porcine oocytes and parthenogenesis. Mol Reprod Dev. 1996;43:513–518. - PubMed
-
- Maro B, Johnson MH, Webb M, Flach G. Mechanism of polar body formation in the mouse oocyte: an interaction between the chromosomes, the cytoskeleton and the plasma membrane. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1986;92:11–32. - PubMed
-
- Longo FJ, Chen DY. Development of cortical polarity in mouse eggs: involvement of the meiotic apparatus. Dev Biol. 1985;107:382–394. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

