Purification and characterization of a cytosolic Ca(2+)-independent phospholipase A(2) from bovine brain
- PMID: 21874539
- PMCID: PMC3887695
- DOI: 10.1007/s10059-011-1058-7
Purification and characterization of a cytosolic Ca(2+)-independent phospholipase A(2) from bovine brain
Abstract
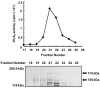
The Ca(2+)-independent phospholipase A(2) (iPLA(2)) subfamily of enzymes is associated with arachidonic acid (AA) release and the subsequent increase in fatty acid turnover. This phenomenon occurs not only during apoptosis but also during inflammation and lymphocyte proliferation. In this study, we purified and characterized a novel type of iPLA(2) from bovine brain. iPLA(2) was purified 4,174-fold from the bovine brain by a sequential process involving DEAE-cellulose anion exchange, phenyl-5PW hydrophobic interaction, heparin-Sepharose affinity, Sephacryl S-300 gel filtration, Mono S cation exchange, Mono Q anion exchange, and Superose 12 gel filtration. A single peak of iPLA(2) activity was eluted at an apparent molecular mass of 155 kDa during the final Superose 12 gel-filtration step. The purified enzyme had an isoelectric point of 5.3 on two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) and was inhibited by arachidonyl trifluoromethyl ketone (AACOCF(3)), Triton X-100, iron, and Ca(2+). However, it was not inhibited by bromoenol lactone (BEL), an inhibitor of iPLA(2), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The spot with the iPLA(2) activity did not match with any known protein sequence, as determined by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) analysis. Altogether, these data suggest that the purified enzyme is a novel form of cytosolic iPLA(2).
Figures



References
-
- Ackermann E.J., Kempner E.S., Dennis E.A. Ca(2+)- independent cytosolic phospholipase A2 from macrophage-like P388D1 cells. Isolation and characterization. Isolation and characterization. J. Biol. Chem. (1994);269:9227–9233. - PubMed
-
- Ackermann E.J., Conde-Frieboes K., Dennis E.A. Inhibition of macrophage Ca(2+)-independent phospholipase A2 by bromoenol lactone and trifluoromethyl ketones. J. Biol. Chem. (1995);270:445–450. - PubMed
-
- Anderson D.K., Saunders R.D., Demediuk P., Dugan L.L., Braughler J.M., Hall E.D., Means E.D., Horrocks L.A. Lipid hydrolysis and peroxidation in injured spinal cord: partial protection with methylprednisolone or vitamin E and selenium. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Trauma. (1985);2:257–267. - PubMed
-
- Bonventre J.V., Huang Z., Taheri M.R., O’Leary E., Li E., Moskowitz M.A., Sapirstein A. Reduced fertility and postischaemic brain injury in mice deficient in cytosolic phospholipase A2. Nature. (1997);390:622–625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

