Temporal discounting of rewards in patients with bipolar disorder and schizophrenia
- PMID: 21875166
- PMCID: PMC3210906
- DOI: 10.1037/a0023333
Temporal discounting of rewards in patients with bipolar disorder and schizophrenia
Abstract
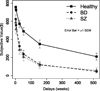
Patients with bipolar disorder (BD) and schizophrenia (SZ) often show decision-making deficits in everyday circumstances. A failure to appropriately weigh immediate versus future consequences of choices may contribute to these deficits. We used the delay discounting task in individuals with BD or SZ to investigate their temporal decision making. Twenty-two individuals with BD, 21 individuals with SZ, and 30 healthy individuals completed the delay discounting task along with neuropsychological measures of working memory and cognitive function. Both BD and SZ groups discounted delayed rewards more steeply than did the healthy group even after controlling for current substance use, age, gender, and employment. Hierarchical multiple regression analyses showed that discounting rate was associated with both diagnostic group and working memory or intelligence scores. In each group, working memory or intelligence scores negatively correlated with discounting rate. The results suggest that (a) both BD and SZ groups value smaller, immediate rewards more than larger, delayed rewards compared with the healthy group and (b) working memory or intelligence is related to temporal decision making in individuals with BD or SZ as well as in healthy individuals.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Task Force on DSM-IV. DSM-IV: diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 1994.
-
- Andreasen NC. The Scale for the Assessment of Negative Symptoms (SANS): conceptual and theoretical foundations. British Journal of Psychiatry. 1989;(7):49–58. - PubMed
-
- Bearden CE, Hoffman KM, Cannon TD. The neuropsychology and neuroanatomy of bipolar affective disorder: a critical review. Bipolar Disorders. 2001;3(3):106. - PubMed
-
- Bickel WK, Odum AL, Madden GJ. Impulsivity and cigarette smoking: delay discounting in current, never, and ex-smokers. Psychopharmacology. 1999;146:447–454. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical