Exploring the bases for a mixed reality stroke rehabilitation system, part I: a unified approach for representing action, quantitative evaluation, and interactive feedback
- PMID: 21875441
- PMCID: PMC3180296
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-0003-8-51
Exploring the bases for a mixed reality stroke rehabilitation system, part I: a unified approach for representing action, quantitative evaluation, and interactive feedback
Abstract
Background: Although principles based in motor learning, rehabilitation, and human-computer interfaces can guide the design of effective interactive systems for rehabilitation, a unified approach that connects these key principles into an integrated design, and can form a methodology that can be generalized to interactive stroke rehabilitation, is presently unavailable.
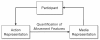
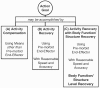
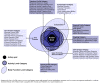
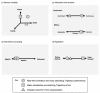
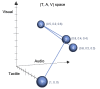
Results: This paper integrates phenomenological approaches to interaction and embodied knowledge with rehabilitation practices and theories to achieve the basis for a methodology that can support effective adaptive, interactive rehabilitation. Our resulting methodology provides guidelines for the development of an action representation, quantification of action, and the design of interactive feedback. As Part I of a two-part series, this paper presents key principles of the unified approach. Part II then describes the application of this approach within the implementation of the Adaptive Mixed Reality Rehabilitation (AMRR) system for stroke rehabilitation.
Conclusions: The accompanying principles for composing novel mixed reality environments for stroke rehabilitation can advance the design and implementation of effective mixed reality systems for the clinical setting, and ultimately be adapted for home-based application. They furthermore can be applied to other rehabilitation needs beyond stroke.
Figures

References
-
- Krakauer JW. Motor learning: its relevance to stroke recovery and neurorehabilitation. Curr Opin Neurol. 2006;19:84–90. doi: 10.1097/01.wco.0000200544.29915.cc. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schmidt RA. In: Contemporary management of motor control problems: Proceedings of the II STEPConference: June 1991; Alexandria. Foundation for Physical Therapy, editor. 1991. Motor learning principles for physical therapy; pp. 49–63.
-
- Richards L, Pohl P. Therapeutic interventions to improve upper extremity recovery and function. Clin Geriatr Med. 1999;15:819–832. - PubMed
-
- Pridmore T, Green J, Hilton D, Eastgate R, Cobb S. Mixed reality environments in stroke rehabilitation: interfaces across the real/virtual divide. Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Disability, Virtual Reality & Associated Technology: 20-22 September 2004; Oxford. 2004.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

