Immune modulation and modulators in Heligmosomoides polygyrus infection
- PMID: 21875581
- PMCID: PMC6485391
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exppara.2011.08.011
Immune modulation and modulators in Heligmosomoides polygyrus infection
Abstract
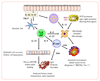
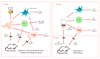
The intestinal nematode parasite Heligmosomoides polygyrus bakeri exerts widespread immunomodulatory effects on both the innate and adaptive immune system of the host. Infected mice adopt an immunoregulated phenotype, with abated allergic and autoimmune reactions. At the cellular level, infection is accompanied by expanded regulatory T cell populations, skewed dendritic cell and macrophage phenotypes, B cell hyperstimulation and multiple localised changes within the intestinal environment. In most mouse strains, these act to block protective Th2 immunity. The molecular basis of parasite interactions with the host immune system centres upon secreted products termed HES (H. polygyrus excretory-secretory antigen), which include a TGF-β-like ligand that induces de novo regulatory T cells, factors that modify innate inflammatory responses, and molecules that block allergy in vivo. Proteomic and transcriptomic definition of parasite proteins, combined with biochemical identification of immunogenic molecules in resistant mice, will provide new candidate immunomodulators and vaccine antigens for future research.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Helminth secretions induce de novo T cell Foxp3 expression and regulatory function through the TGF-β pathway.J Exp Med. 2010 Oct 25;207(11):2331-41. doi: 10.1084/jem.20101074. Epub 2010 Sep 27. J Exp Med. 2010. PMID: 20876311 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of type 2 immunity and allergic airway inflammation by secreted products of the helminth Heligmosomoides polygyrus.Eur J Immunol. 2012 Oct;42(10):2667-82. doi: 10.1002/eji.201142161. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Eur J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22706967 Free PMC article.
-
Novel O-linked methylated glycan antigens decorate secreted immunodominant glycoproteins from the intestinal nematode Heligmosomoides polygyrus.Int J Parasitol. 2016 Mar;46(3):157-170. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2015.10.004. Epub 2015 Dec 12. Int J Parasitol. 2016. PMID: 26688390 Free PMC article.
-
Immunity to the model intestinal helminth parasite Heligmosomoides polygyrus.Semin Immunopathol. 2012 Nov;34(6):829-46. doi: 10.1007/s00281-012-0347-3. Epub 2012 Oct 11. Semin Immunopathol. 2012. PMID: 23053394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-mediated regulation of immune responses to intestinal helminth infections.Parasite Immunol. 2017 Feb;39(2). doi: 10.1111/pim.12406. Parasite Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27977850 Review.
Cited by
-
The helminth community component species of the wood mouse as biological tags of a ten post-fire-year regeneration process in a Mediterranean ecosystem.Parasitol Res. 2018 Jul;117(7):2217-2231. doi: 10.1007/s00436-018-5909-4. Epub 2018 May 10. Parasitol Res. 2018. PMID: 29744702
-
Helminth-induced alterations of the gut microbiota exacerbate bacterial colitis.Mucosal Immunol. 2018 Jan;11(1):144-157. doi: 10.1038/mi.2017.20. Epub 2017 Mar 29. Mucosal Immunol. 2018. PMID: 28352104 Free PMC article.
-
Susceptibility to Ticks and Lyme Disease Spirochetes Is Not Affected in Mice Coinfected with Nematodes.Infect Immun. 2016 Apr 22;84(5):1274-1286. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01309-15. Print 2016 May. Infect Immun. 2016. PMID: 26883594 Free PMC article.
-
Helminth-Induced and Th2-Dependent Alterations of the Gut Microbiota Attenuate Obesity Caused by High-Fat Diet.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;10(4):763-778. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2020.06.010. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32629118 Free PMC article.
-
HpARI Protein Secreted by a Helminth Parasite Suppresses Interleukin-33.Immunity. 2017 Oct 17;47(4):739-751.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.09.015. Immunity. 2017. PMID: 29045903 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali NM, Behnke JM. Nematospiroides dubius: factors affecting the primary response to SRBC in infected mice. J Helminthol. 1983;57:343–353. - PubMed
-
- Ali NMH, Behnke JM. Non-specific immunodepression by larval and adult Nematospiroides dubius. Parasitology. 1984;88:153–162. - PubMed
-
- Allen JE, Maizels RM. Diversity and dialogue in immunity to helminths. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11:375–388. - PubMed
-
- Anjuère F, Luci C, Lebens M, Rousseau D, Hervouet C, Milon G, Holmgren J, Ardavin C, Czerkinsky C. In vivo adjuvant-induced mobilization and maturation of gut dendritic cells after oral administration of cholera toxin. J Immunol. 2004;173:5103–5111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources