The COMPASS family of H3K4 methylases in Drosophila
- PMID: 21875999
- PMCID: PMC3209330
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.06092-11
The COMPASS family of H3K4 methylases in Drosophila
Abstract
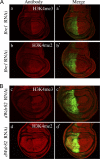
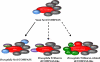
Methylation of histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is implemented by Set1/COMPASS, which was originally purified based on the similarity of yeast Set1 to human MLL1 and Drosophila melanogaster Trithorax (Trx). While humans have six COMPASS family members, Drosophila possesses a representative of the three subclasses within COMPASS-like complexes: dSet1 (human SET1A/SET1B), Trx (human MLL1/2), and Trr (human MLL3/4). Here, we report the biochemical purification and molecular characterization of the Drosophila COMPASS family. We observed a one-to-one similarity in subunit composition with their mammalian counterparts, with the exception of LPT (lost plant homeodomains [PHDs] of Trr), which copurifies with the Trr complex. LPT is a previously uncharacterized protein that is homologous to the multiple PHD fingers found in the N-terminal regions of mammalian MLL3/4 but not Drosophila Trr, indicating that Trr and LPT constitute a split gene of an MLL3/4 ancestor. Our study demonstrates that all three complexes in Drosophila are H3K4 methyltransferases; however, dSet1/COMPASS is the major monoubiquitination-dependent H3K4 di- and trimethylase in Drosophila. Taken together, this study provides a springboard for the functional dissection of the COMPASS family members and their role in the regulation of histone H3K4 methylation throughout development in Drosophila.
Figures



References
-
- Bernstein B. E., et al. 2005. Genomic maps and comparative analysis of histone modifications in human and mouse. Cell 120:169–181 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
