Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacogenetics of hydroxyurea treatment for children with sickle cell anemia
- PMID: 21876119
- PMCID: PMC3208303
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-07-364190
Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacogenetics of hydroxyurea treatment for children with sickle cell anemia
Abstract
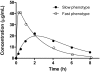
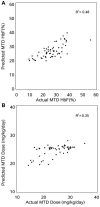
Hydroxyurea therapy has proven laboratory and clinical efficacies for children with sickle cell anemia (SCA). When administered at maximum tolerated dose (MTD), hydroxyurea increases fetal hemoglobin (HbF) to levels ranging from 10% to 40%. However, interpatient variability of percentage of HbF (%HbF) response is high, MTD itself is variable, and accurate predictors of hydroxyurea responses do not currently exist. HUSTLE (NCT00305175) was designed to provide first-dose pharmacokinetics (PK) data for children with SCA initiating hydroxyurea therapy, to investigate pharmacodynamics (PD) parameters, including HbF response and MTD after standardized dose escalation, and to evaluate pharmacogenetics influences on PK and PD parameters. For 87 children with first-dose PK studies, substantial interpatient variability was observed, plus a novel oral absorption phenotype (rapid or slow) that influenced serum hydroxyurea levels and total hydroxyurea exposure. PD responses in 174 subjects were robust and similar to previous cohorts; %HbF at MTD was best predicted by 5 variables, including baseline %HbF, whereas MTD was best predicted by 5 variables, including serum creatinine. Pharmacogenetics analysis showed single nucleotide polymorphisms influencing baseline %HbF, including 5 within BCL11A, but none influencing MTD %HbF or dose. Accurate prediction of hydroxyurea treatment responses for SCA remains a worthy but elusive goal.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictors of fetal hemoglobin response in children with sickle cell anemia receiving hydroxyurea therapy.Blood. 2002 Jan 1;99(1):10-4. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.1.10. Blood. 2002. PMID: 11756146 Clinical Trial.
-
Whole exome sequencing identifies novel genes for fetal hemoglobin response to hydroxyurea in children with sickle cell anemia.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 31;9(10):e110740. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110740. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25360671 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Early initiation of hydroxyurea (hydroxycarbamide) using individualised, pharmacokinetics-guided dosing can produce sustained and nearly pancellular expression of fetal haemoglobin in children with sickle cell anaemia.Br J Haematol. 2021 Aug;194(3):617-625. doi: 10.1111/bjh.17663. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Br J Haematol. 2021. PMID: 34227124 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Changing the Clinical Paradigm of Hydroxyurea Treatment for Sickle Cell Anemia Through Precision Medicine.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Jan;109(1):73-81. doi: 10.1002/cpt.2028. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 32869281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Do Genetic Polymorphisms Affect Fetal Hemoglobin (HbF) Levels in Patients With Sickle Cell Anemia Treated With Hydroxyurea? A Systematic Review and Pathway Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 21;12:779497. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.779497. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35126118 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence and cost of sickle cell disease in France: real-world analysis using data from the Echantillon Généraliste des Bénéficiaires.Front Public Health. 2023 Sep 21;11:1215605. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1215605. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37808997 Free PMC article.
-
Novel clinical care models for patients with sickle cell disease.Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2024 Dec 6;2024(1):618-622. doi: 10.1182/hematology.2024000586. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2024. PMID: 39644018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stable-Isotope Dilution HPLC-Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Quantifying Hydroxyurea in Dried Blood Samples.Clin Chem. 2016 Dec;62(12):1593-1601. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2016.263715. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Clin Chem. 2016. PMID: 27694393 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxyurea Treatment and Development of the Rat Cerebellum: Effects on the Neurogenetic Profiles and Settled Patterns of Purkinje Cells and Deep Cerebellar Nuclei Neurons.Neurotox Res. 2016 Nov;30(4):563-580. doi: 10.1007/s12640-016-9649-x. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Neurotox Res. 2016. PMID: 27401826
-
Genetic modifiers of fetal hemoglobin affect the course of sickle cell disease in patients treated with hydroxyurea.Haematologica. 2022 Jul 1;107(7):1577-1588. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2021.278952. Haematologica. 2022. PMID: 34706496 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ware RE, Aygun B. Advances in the use of hydroxyurea. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2009:62–69. - PubMed
-
- Charache S, Dover GH, Moore RD, et al. Hydroxyurea: effects on hemoglobin F production in patients with sickle cell anemia. Blood. 1992;79(10):2555–2565. - PubMed
-
- Kinney TR, Helms RW, O'Branksi EE, et al. Safety of hydroxyurea in children with sickle cell anemia: results of the HUG-KIDS study, a phase I/II trial. Pediatric Hydroxyurea Group. Blood. 1999;94(5):1550–1554. - PubMed
-
- Zimmerman SA, Schultz WH, Davis JS, et al. Sustained long-term hematologic efficacy of hydroxyurea at maximum tolerated dose in children with sickle cell disease. Blood. 2004;103(6):2039–2045. - PubMed

