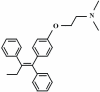
Tumorigenic effects of tamoxifen on the female genital tract
- PMID: 21876648
- PMCID: PMC3160006
- DOI: 10.4137/cpath.s487
Tumorigenic effects of tamoxifen on the female genital tract
Abstract
Tamoxifen is widely used for endocrine treatment and breast cancer prevention. It acts as both an estrogen antagonist in breast tissue and an estrogen agonist in the female lower genital tract. Tamoxifen causes severe gynecologic side effects, such as endometrial cancer. This review focuses on the effects of prolonged tamoxifen treatment on the human female genital tract and considers its tumorigenicity in the gynecologic organs through clinical data analysis. Tamoxifen is associated with an increased incidence of benign endometrial lesions such as polyps and hyperplasia and a two- to four-fold increased risk of endometrial cancer in postmenopausal patients. Moreover, the incidence of functional ovarian cysts is significantly high in premenopausal tamoxifen users. To prevent tamoxifen from having severe side effects in gynecologic organs, frequent gynecological examination should be performed for both premenopausal and postmenopausal patients with breast cancer who are treated with this drug.
Keywords: breast cancer; estrogenicity; ovary; tamoxifen; tumorigenicity; uterus.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tamoxifen treatment and gynecologic side effects: a review.Obstet Gynecol. 2001 May;97(5 Pt 2):855-66. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(00)01196-0. Obstet Gynecol. 2001. PMID: 11336777 Review.
-
Effects of tamoxifen on the human female genital tract: review of the literature.Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2003;24(3-4):258-68. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12807236 Review.
-
Benign gynecologic conditions among participants in the Breast Cancer Prevention Trial.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005 Apr;192(4):1230-7; discussion 1237-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2004.12.083. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005. PMID: 15846210 Clinical Trial.
-
Utilization of gynecologic services in women with breast cancer receiving hormonal therapy.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017 Jul;217(1):59.e1-59.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2017.03.011. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017. PMID: 28341383 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of Endometrial Polyps, Hyperplasia, Carcinoma, and Uterine Cancer After Tamoxifen Treatment in Premenopausal Women With Breast Cancer.JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Nov 1;5(11):e2243951. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.43951. JAMA Netw Open. 2022. PMID: 36441547 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Benign Metastasizing Leiomyomatosis to the Skin and Lungs, Intravenous Leiomyomatosis, and Leiomyomatosis Peritonealis Disseminata: A Series of Five Cases.Oncologist. 2022 Feb 3;27(1):e89-e98. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyab019. Oncologist. 2022. PMID: 35305104 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of life in relation to tamoxifen or exemestane treatment in postmenopausal breast cancer patients: a Tamoxifen Exemestane Adjuvant Multinational (TEAM) Trial side study.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Jul;134(1):267-76. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-2028-2. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 22453754 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Effect of Tamoxifen Citrate on Granulosa Cells of Ovarian Follicles in Adult Female Rats: Light Microscopic Study.J Microsc Ultrastruct. 2022 Nov 9;12(1):1-5. doi: 10.4103/jmau.jmau_79_21. eCollection 2024 Jan-Mar. J Microsc Ultrastruct. 2022. PMID: 38633571 Free PMC article.
-
Secretory Endometrial Adenocarcinoma: A Rare Sequelae in a Postmenopausal Woman Following Tamoxifen Therapy for Breast Cancer.J Midlife Health. 2020 Jul-Sep;11(3):171-174. doi: 10.4103/jmh.JMH_104_19. Epub 2020 Sep 29. J Midlife Health. 2020. PMID: 33384542 Free PMC article.
-
BreastDefend enhances effect of tamoxifen in estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer in vitro and in vivo.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Feb 16;17(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1621-7. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28209156 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ACOG Committee Opinion Tamoxifen and endometrial cancer. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 1996;53:197–9. - PubMed
-
- ACOG Committee Opinion Tamoxifen and uterine cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 2006;107:1475–8. - PubMed
-
- Altaner S, Zgucer F, Tokatli F, et al. Expression of Bcl-2 and Ki-67 in tamoxifen-associated endometrial polyps: comparison with postmenopausal polyps. Onkologie. 2006;29:376–80. - PubMed
-
- Altaras MM, Aviram R, Cohen I, et al. Role of prolonged stimulation of tamoxifen therapy in the etiology of endometrial sarcomas. Gynecol Oncol. 1993;49:255–8. - PubMed
-
- Ascher SM, Imaoka I, Lage JM. Tamoxifen-induced uterine abnormalities: the role of imaging. Radiology. 2000;214:29–38. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

