Language and cognition interaction neural mechanisms
- PMID: 21876687
- PMCID: PMC3163128
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/454587
Language and cognition interaction neural mechanisms
Abstract
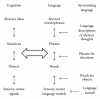
How language and cognition interact in thinking? Is language just used for communication of completed thoughts, or is it fundamental for thinking? Existing approaches have not led to a computational theory. We develop a hypothesis that language and cognition are two separate but closely interacting mechanisms. Language accumulates cultural wisdom; cognition develops mental representations modeling surrounding world and adapts cultural knowledge to concrete circumstances of life. Language is acquired from surrounding language "ready-made" and therefore can be acquired early in life. This early acquisition of language in childhood encompasses the entire hierarchy from sounds to words, to phrases, and to highest concepts existing in culture. Cognition is developed from experience. Yet cognition cannot be acquired from experience alone; language is a necessary intermediary, a "teacher." A mathematical model is developed; it overcomes previous difficulties and leads to a computational theory. This model is consistent with Arbib's "language prewired brain" built on top of mirror neuron system. It models recent neuroimaging data about cognition, remaining unnoticed by other theories. A number of properties of language and cognition are explained, which previously seemed mysterious, including influence of language grammar on cultural evolution, which may explain specifics of English and Arabic cultures.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Brain. Conscious and unconscious mechanisms of cognition, emotions, and language.Brain Sci. 2012 Dec 18;2(4):790-834. doi: 10.3390/brainsci2040790. Brain Sci. 2012. PMID: 24961270 Free PMC article.
-
Mirror neurons, language, and embodied cognition.Neural Netw. 2013 May;41:15-22. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2013.01.003. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Neural Netw. 2013. PMID: 23403367
-
Language and emotions: emotional Sapir-Whorf hypothesis.Neural Netw. 2009 Jul-Aug;22(5-6):518-26. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2009.06.034. Epub 2009 Jul 2. Neural Netw. 2009. PMID: 19616406 Review.
-
Language is handy but is it embodied?Neuropsychologia. 2014 Mar;55:57-70. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2013.11.004. Epub 2013 Nov 16. Neuropsychologia. 2014. PMID: 24252354 Review.
-
Musical emotions: functions, origins, evolution.Phys Life Rev. 2010 Mar;7(1):2-27. doi: 10.1016/j.plrev.2009.11.001. Epub 2009 Nov 6. Phys Life Rev. 2010. PMID: 20374916 Review.
Cited by
-
Data-driven machine learning models for decoding speech categorization from evoked brain responses.J Neural Eng. 2021 Mar 23;18(4):10.1088/1741-2552/abecf0. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/abecf0. J Neural Eng. 2021. PMID: 33690177 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese-English bilinguals show linguistic-perceptual links in the brain associating short spoken phrases with corresponding real-world natural action sounds by semantic category.Lang Cogn Neurosci. 2021;36(6):773-790. doi: 10.1080/23273798.2021.1883073. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Lang Cogn Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34568509 Free PMC article.
-
Physics of the Mind.Front Syst Neurosci. 2016 Nov 15;10:84. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2016.00084. eCollection 2016. Front Syst Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27895558 Free PMC article.
-
Brain. Conscious and unconscious mechanisms of cognition, emotions, and language.Brain Sci. 2012 Dec 18;2(4):790-834. doi: 10.3390/brainsci2040790. Brain Sci. 2012. PMID: 24961270 Free PMC article.
-
Aesthetic Chills: Knowledge-Acquisition, Meaning-Making, and Aesthetic Emotions.Front Psychol. 2016 Aug 4;7:1093. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01093. eCollection 2016. Front Psychol. 2016. PMID: 27540366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gödel K. In: Collected Works. Feferman S, Dawson JW Jr., Kleene SC, editors. New York, NY, USA: Oxford University Press; 1931–1994.
-
- Chomsky N. Aspects of the Theory of Syntax. Cambridge, UK: MIT Press; 1965.
-
- Chomsky N. Principles and parameters in syntactic theory. In: Hornstein N, Lightfoot D, editors. Explanation in Linguistics. The Logical Problem of Language Acquisition. London, UK: Longman; 1981.
-
- Chomsky N. The Minimalist Program. Cambridge, UK: MIT Press; 1995.
-
- Croft W, Alan C. Cognitive Linguistics. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; 2004.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

