How to recondition ex vivo initially rejected donor lungs for clinical transplantation: clinical experience from lund university hospital
- PMID: 21876780
- PMCID: PMC3163037
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/754383
How to recondition ex vivo initially rejected donor lungs for clinical transplantation: clinical experience from lund university hospital
Abstract
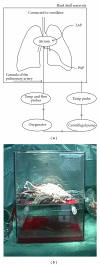
A major problem in clinical lung transplantation is the shortage of donor lungs. Only about 20% of donor lungs are accepted for transplantation. We have recently reported the results of the first six double lung transplantations performed with donor lungs reconditioned ex vivo that had been deemed unsuitable for transplantation by the Scandiatransplant, Eurotransplant, and UK Transplant organizations because the arterial oxygen pressure was less than 40 kPa. The three-month survival of patients undergoing transplant with these lungs was 100%. One patient died due to sepsis after 95 days, and one due to rejection after 9 months. Four recipients are still alive and well 24 months after transplantation, with no signs of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome. The donor lungs were reconditioned ex vivo in an extracorporeal membrane oxygenation circuit using STEEN solution mixed with erythrocytes, to dehydrate edematous lung tissue. Functional evaluation was performed with deoxygenated perfusate at different inspired fractions of oxygen. The arterial oxygen pressure was significantly improved in this model. This ex vivo evaluation model is thus a valuable addition to the armamentarium in increasing the number of acceptable lungs in a donor population with inferior arterial oxygen pressure values, thereby, increasing the lung donor pool for transplantation. In the following paper we present our clinical experience from the first six patients in the world. We also present the technique we used in detail with flowchart.
Figures




References
-
- Punch JD, Hayes DH, Laporte FB, McBride V, Seely MS. Organ donation and utilization in the United States, 1996–2005. American Journal of Transplantation. 2007;7(1):1327–1338. - PubMed
-
- Trulock EP, Edwards LB, Taylor DO, Boucek MM, Keck BM, Hertz MI. The registry of the international society for heart and lung transplantation: twenty-first official adult lung and heart-lung transplant report—2004. Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation. 2004;23(7):804–815. - PubMed
-
- Hertz MI, Taylor DO, Trulock EP, et al. The registry of the international society for Heart And Lung transplantation: nineteenth official report—2002. Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation. 2002;21(9):950–970. - PubMed
-
- Novitzky D, Wicomb WN, Rose AG. Pathophysiology of pulmonary edema following experimental brain death in the chacma baboon. Annals of Thoracic Surgery. 1987;43(3):288–294. - PubMed
-
- Guyton A, Hall J. Textbook of Medical Physiology. 11th edition. Philadelphia, Pa, USA: Elsevier Saunders; 2006.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

