Redox regulation of cytokeratin 18 protein by NADPH oxidase 1 in preneoplastic human epithelial cells
- PMID: 21877197
- PMCID: PMC11827927
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-011-1041-x
Redox regulation of cytokeratin 18 protein by NADPH oxidase 1 in preneoplastic human epithelial cells
Abstract
Introduction: A catalytic subunit of NADPH oxidase 1 (Nox1) is implicated to be involved in neoplastic progression in human epithelial cancers. We had previously demonstrated that Nox1 overexpression of immortalized epithelial cells was able to induce the generation of progenitor cells that expressed fetal-type cytokeratins 8 and 18.
Purpose: We aimed to investigate the direct effects and underlying mechanisms of Nox1 on expression of cytokeratin 18 (CK18).
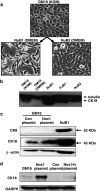
Methods: Immortalized human epithelial GM16 cells with low CK18 were used in Nox1 overexpression experiments. NuB2 cells with high CK18 were used in Nox1 knockdown experiments. Protein expression of CK18, phosphorylated and ubiquitinated CK18 were analyzed by Western blot.
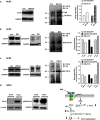
Results: With no effects on the mRNA levels, CK18 protein was increased upon Nox1 overexpression and decreased upon Nox1 knockdown. Treatment with proteasome inhibitor MG132 prevented CK18 degradation and increased CK18 protein indicating translational regulation of CK18. Treatment for NuB2 cells with N-acetyl-L: -cysteine, diphenyleneiodonium, or apocynin decreased CK18 protein levels indicating its regulation involving reactive oxygen species and flavoprotein Nox. It has been known that phosphorylation of CK18 regulates CK18 turnover by ubiquination. Consistently, Nox1 modulated CK18 phosphorylation at ser52. Nox1 knockdown and treatment with diphenyleneiodonium accumulated the levels of ubiquinated CK18 enhancing degradation causing decreased CK18 protein.
Conclusion: We demonstrated that Nox1 was able to induce CK18 stabilization by inhibiting CK18 protein degradation in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. CK18 accumulation induced by Nox1 is consistent with the persistence of fetal-type CK18 protein in many epithelial carcinomas.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interests to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Bánfi B, Maturana A, Jaconi S, Arnaudeau S, Laforge T, Sinha B, Ligeti E, Demaurex N, Krause KH (2000) A mammalian H+ channel generated through alternative splicing of the NADPH oxidase homolog NOH-1. Science 287:138–142 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

