The dysregulation of cytokine networks in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 21877904
- PMCID: PMC3189553
- DOI: 10.1089/jir.2011.0029
The dysregulation of cytokine networks in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
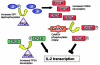
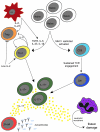
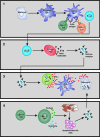
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease associated with chronic immune activation and tissue damage. Organ damage in SLE results from the deposition of immune complexes and the infiltration of activated T cells into susceptible organs. Cytokines are intimately involved in every step of the SLE pathogenesis. Defective immune regulation and uncontrolled lymphocyte activation, as well as increased antigen presenting cell maturation are all influenced by cytokines. Moreover, expansion of local immune responses as well as tissue infiltration by pathogenic cells is instigated by cytokines. In this review, we describe the main cytokine abnormalities reported in SLE and discuss the mechanisms that drive their aberrant production as well as the pathogenic pathways that their presence promotes.
Figures
References
-
- Agrawal H. Jacob N. Carreras E. Bajana S. Putterman C. Turner S. Neas B. Mathian A. Koss MN. Stohl W. Kovats S. Jacob CO. Deficiency of type I IFN receptor in lupus-prone New Zealand mixed 2328 mice decreases dendritic cell numbers and activation and protects from disease. J Immunol. 2009;183:6021–6029. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aringer M. Stummvoll GH. Steiner G. Koller M. Steiner CW. Hofler E. Hiesberger H. Smolen JS. Graninger WB. Serum interleukin-15 is elevated in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2001;40:876–881. - PubMed
-
- Awasthi A. Carrier Y. Peron JP. Bettelli E. Kamanaka M. Flavell RA. Kuchroo VK. Oukka M. Weiner HL. A dominant function for interleukin 27 in generating interleukin 10-producing anti-inflammatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:1380–1389. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

