Strain differences in seizure-induced cell death following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus
- PMID: 21878392
- PMCID: PMC3225715
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2011.08.013
Strain differences in seizure-induced cell death following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus
Abstract
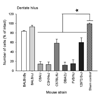
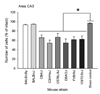
Mouse strains differ from one another in their susceptibility to seizure-induced excitotoxic cell death. Previously, we have demonstrated that mature inbred strains of mice show remarkable genetic differences in susceptibility to the neuropathological consequences of seizures in the kainate model of status epilepticus. At present, while the cellular mechanisms underlying strain-dependent differences in susceptibility remain unclear, some of this variation is assumed to have a genetic basis. However, it remains unclear whether strain differences in susceptibility to seizure-induced cell death observed following kainate administration are observed following systemic administration of other chemoconvulsants. In rodents, the cholinomimetic convulsant pilocarpine is widely used to induce status epilepticus (SE), followed by hippocampal damage and spontaneous recurrent seizures, resembling temporal lobe epilepsy. This model has initially been described in rats, but is increasingly used in mice. We characterized neuronal pathologies after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus (SE) in eight inbred strains of mice focusing on the hippocampus. A ramping-up dose protocol for pilocarpine was used and behavior was monitored for 4-5 h. While we did not observe any significant differences in seizure latency or duration to pilocarpine among the inbred strains, we did observe a significant difference in susceptibility to the neuropathological consequences of pilocarpine-induced SE. Of the eight genetically diverse mouse strains screened for pilocarpine-induced status, BALB/cJ and BALB/cByJ were the only two strains that were resistant to the neuropathological consequences of seizure-induced cell death. Additional studies of these murine strains may be useful for investigating genetic influences on pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Babb TL, Kupfer WR, Pretorius JK, Crandall PH, Levesque MF. Synaptic reorganization by mossy fibers in human epileptic fascia dentate. Neuroscience. 1991;42:351–363. - PubMed
-
- Berkovic SF, Mulley JC, Scheffer IE, Petrou S. Human epilepsies: interaction of genetic and acquired factors. Trends Neurosci. 2006;29:391–397. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y. Limbic seizure and brain damage produced by kainic acid: mechanisms and relevance to human temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroscience. 1985;14:375–403. - PubMed
-
- Berger ML, Lefauconnier JM, Tremblay E, Ben-Ari Y. Limbic seizures induced by systemically applied kainic acid: how much kainic acid reaches the brain? Adv Exp Med Biol. 1986;203:199–209. - PubMed
-
- Borges K, Gearing M, McDermott DL, Smith AB, Almonte AG, Wainer BH, Dingledine R. Neuronal and glial pathological changes during epileptogenesis in the mouse pilocarpine model. Exp Neurol. 2003;182:21–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

