Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC)--a powerful separation technique
- PMID: 21879300
- PMCID: PMC3249561
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-011-5308-5
Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC)--a powerful separation technique
Abstract
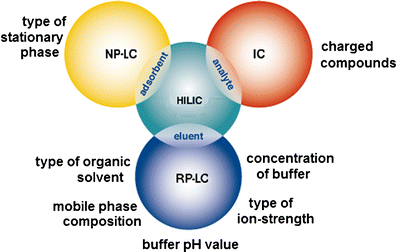
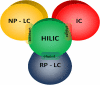
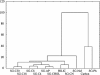
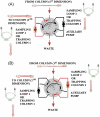
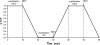
Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) provides an alternative approach to effectively separate small polar compounds on polar stationary phases. The purpose of this work was to review the options for the characterization of HILIC stationary phases and their applications for separations of polar compounds in complex matrices. The characteristics of the hydrophilic stationary phase may affect and in some cases limit the choices of mobile phase composition, ion strength or buffer pH value available, since mechanisms other than hydrophilic partitioning could potentially occur. Enhancing our understanding of retention behavior in HILIC increases the scope of possible applications of liquid chromatography. One interesting option may also be to use HILIC in orthogonal and/or two-dimensional separations. Bioapplications of HILIC systems are also presented.
Figures


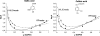


Similar articles
-
Effect of silica gel modification with cyclofructans on properties of hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography stationary phases.J Chromatogr A. 2012 Sep 28;1257:58-65. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2012.08.004. Epub 2012 Aug 13. J Chromatogr A. 2012. PMID: 22921504
-
[Stationary phases for hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography and their applications in separation of traditional Chinese medicines].Se Pu. 2009 Sep;27(5):675-81. Se Pu. 2009. PMID: 20073204 Review. Chinese.
-
Sulfonated cyclofructan 6 based stationary phase for hydrophilic interaction chromatography.J Sep Sci. 2011 Jul;34(14):1636-47. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201100121. Epub 2011 Jun 24. J Sep Sci. 2011. PMID: 21710525
-
Peptide retention time prediction for hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography at acidic pH in formic-acid based eluents.J Chromatogr A. 2024 Nov 8;1736:465355. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2024.465355. Epub 2024 Sep 7. J Chromatogr A. 2024. PMID: 39260150
-
Retention and selectivity of stationary phases for hydrophilic interaction chromatography.J Chromatogr A. 2011 Sep 2;1218(35):5920-38. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2011.06.052. Epub 2011 Jun 21. J Chromatogr A. 2011. PMID: 21737083 Review.
Cited by
-
Methods of Lipidomic Analysis: Extraction, Derivatization, Separation, and Identification of Lipids.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1280:173-187. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-51652-9_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33791982
-
Clinical glycoproteomics: methods and diseases.MedComm (2020). 2024 Oct 4;5(10):e760. doi: 10.1002/mco2.760. eCollection 2024 Oct. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39372389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of different hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography stationary phases on method performance for the determination of highly polar anionic pesticides in complex feed matrices.J Sep Sci. 2021 Jun;44(11):2165-2176. doi: 10.1002/jssc.202001134. Epub 2021 May 4. J Sep Sci. 2021. PMID: 33760354 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Isocratic RP-HPLC Method for Separation and Quantification of L-Citrulline and L-Arginine in Watermelons.Int J Anal Chem. 2018 May 2;2018:4798530. doi: 10.1155/2018/4798530. eCollection 2018. Int J Anal Chem. 2018. PMID: 29853897 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of a stability-indicating hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatographic method for the quantitative determination of vitamin k3 (menadione sodium bisulfite) in injectable solution formulation.Sci Pharm. 2013 May 9;81(3):733-47. doi: 10.3797/scipharm.1303-05. Print 2013 Jul-Sep. Sci Pharm. 2013. PMID: 24106670 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jaroniec M. J Chromatogr A. 1993;656:37–50.
-
- Gritti F, Félix G, Achard MF, Hardouin F. J Chromatogr A. 2001;922:51–61. - PubMed
-
- Wolcott RG, Dolan JW, Snyder LR, Bakalyar SR, Arnold MA, Nichols JA. J Chromatogr A. 2000;869:211–230. - PubMed
-
- Krupczyńska K, Buszewski B, Jandera P. Anal Chem. 2004;76:226–234. - PubMed
-
- Jandera P (2005) Liquid chromatography—normal phase. In: Encyclopedia of analytical science, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 142–152
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

