Long-term results after Boston brace treatment in late-onset juvenile and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
- PMID: 21880123
- PMCID: PMC3189160
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-7161-6-18
Long-term results after Boston brace treatment in late-onset juvenile and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
Abstract
Background: It is recommended that research in patients with idiopathic scoliosis should focus on short- and long-term patient-centred outcome. The aim of the present study was to evaluate outcome in patients with late-onset juvenile or adolescent idiopathic scoliosis 16 years or more after Boston brace treatment.
Methods: 272 (78%) of 360 patients, 251 (92%) women, responded to follow-up examination at a mean of 24.7 (range 16 - 32) years after Boston brace treatment. Fifty-eight (21%) patients had late-onset juvenile and 214 had adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. All patients had clinical and radiological examination and answered a standardised questionnaire including work status, demographics, General Function Score (GFS) (100 - worst possible) and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) (100 - worst possible), EuroQol (EQ-5D) (1 - best possible), EQ-VAS (100 - best possible), and Scoliosis Research Society - 22 (SRS - 22) (5 - best possible).
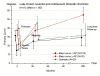
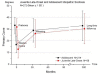
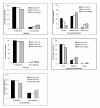
Results: The mean age at follow-up was 40.4 (31-48) years. The prebrace major curve was in average 33.2 (20 - 57)°. At weaning and at the last follow-up the corresponding values were 28.3 (1 - 58)° and 32.5 (7 - 80)°, respectively. Curve development was similar in patients with late-onset juvenile and adolescent start. The prebrace curve increased > 5° in 31% and decreased > 5° in 26%. Twenty-five patients had surgery. Those who did not attend follow-up (n = 88) had a lower mean curve at weaning: 25.4 (6-53)°. Work status was 76% full-time and 10% part-time. Eighty-seven percent had delivered a baby, 50% had pain in pregnancy. The mean (SD) GFS was 7.4 (10.8), ODI 9.3 (11.0), EQ-5D 0.82 (0.2), EQ-VAS 77.6 (17.8), SRS-22: pain 4.1 (0.8), mental health 4.1 (0.6), self-image 3.7 (0.7), function 4.0 (0.6), satisfaction with treatment 3.7 (1.0). Surgical patients had significantly reduced scores for SRS-physical function and self-image, and patients with curves ≥ 45° had reduced self-image.
Conclusion: Long-term results were satisfactory in most braced patients and similar in late-onset juvenile and idiopathic adolescent scoliosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long-term results after Boston brace treatment in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.Scoliosis. 2009 Aug 26;4:17. doi: 10.1186/1748-7161-4-17. Scoliosis. 2009. PMID: 19709435 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term results after brace treatment with Progressive Action Short Brace in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2021 Jun;57(3):406-413. doi: 10.23736/S1973-9087.20.06129-8. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2021. PMID: 32990686
-
Heath-related quality of life and functional outcomes in patients with congenital or juvenile idiopathic scoliosis after an average follow-up of 25 years: a cohort study.Spine J. 2024 Mar;24(3):462-471. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2023.11.012. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Spine J. 2024. PMID: 38029931
-
Health-related quality of life in patients 40 years after diagnosis of an idiopathic scoliosis.Bone Joint J. 2023 Feb;105-B(2):166-171. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.105B2.BJJ-2022-0897.R1. Bone Joint J. 2023. PMID: 36722050 Review.
-
Cotrel-Dubousset (CD) or Universal Spine System (USS) instrumentation in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS): comparison of midterm clinical, functional, and radiologic outcomes.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004 Sep 15;29(18):2024-30. doi: 10.1097/01.brs.0000138408.64907.dc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004. PMID: 15371703 Review.
Cited by
-
Spinal mobility and muscle function in middle-aged patients treated for early onset idiopathic scoliosis: compared with untreated and treated adolescent onset patients.Spine Deform. 2022 Sep;10(5):1085-1095. doi: 10.1007/s43390-022-00487-8. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Spine Deform. 2022. PMID: 35320580 Free PMC article.
-
Can we predict the behavior of the scoliotic curve after bracing in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis? Τhe prognostic value of apical vertebra rotation.Spine Deform. 2021 Jan;9(1):91-98. doi: 10.1007/s43390-020-00184-4. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Spine Deform. 2021. PMID: 32839925
-
Exploration of Contributory Factors to an Unpleasant Bracing Experience of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Patients a Quantitative and Qualitative Research.Children (Basel). 2022 Apr 28;9(5):635. doi: 10.3390/children9050635. Children (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35626812 Free PMC article.
-
Early weaning in idiopathic scoliosis.Scoliosis. 2015 Nov 19;10:32. doi: 10.1186/s13013-015-0059-2. eCollection 2015. Scoliosis. 2015. PMID: 26587052 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of life of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients under brace treatment: a brief communication of literature review.Qual Life Res. 2021 Mar;30(3):703-711. doi: 10.1007/s11136-020-02671-7. Epub 2020 Oct 24. Qual Life Res. 2021. PMID: 33098493 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Negrini S, Minozzi S, Bettany-Saltikov J, Zaina F, Chockalingam N, Grivas TB, Kotwicki T, Maruyama T, Romano M, Vasiliadis ES. Braces for Idiopathic Scoliosis in Adolescents. Spine. 2010;35:1285–1293. - PubMed
-
- Wong MS. Re: Wong MS, Cheng JC, Lam TP, et al. The effect of rigid versus flexible spinal orthosis on the clinical efficacy and acceptance of the patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 2008;33:1360-5. Reply. Spine. 2008;33:2837–2838. - PubMed
-
- Nachemson AL, Peterson LE. Effectiveness of treatment with a brace in girls who have adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. A prospective, controlled study based on data from the Brace Study of the Scoliosis Research Society. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77:815–822. - PubMed
-
- Danielsson AJ, Nachemson AL. Radiologic findings and curve progression 22 years after treatment for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: comparison of brace and surgical treatment with matching control group of straight individuals. Spine. 2001;26:516–525. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200103010-00015. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

