Mesothelin confers pancreatic cancer cell resistance to TNF-α-induced apoptosis through Akt/PI3K/NF-κB activation and IL-6/Mcl-1 overexpression
- PMID: 21880146
- PMCID: PMC3175472
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-106
Mesothelin confers pancreatic cancer cell resistance to TNF-α-induced apoptosis through Akt/PI3K/NF-κB activation and IL-6/Mcl-1 overexpression
Abstract
Background: Previous studies showed that mesothelin (MSLN) plays important roles in survival of pancreatic cancer (PC) cells under anchorage dependent/independent conditions as well as resistance to chemotherapy. The recent success of intratumorally-injected adeno-encoded, chemo/radiation-inducible-promoter driven hTNF-α, (TNFerade) + gemcitabine in pre-clinical models of PC have renewed interest in use of TNF-α as a therapeutic component. To help find additional factors which might affect the therapy, we examined the resistance of MSLN-overexpressing pancreatic cancer cell lines to TNF-α-induced growth inhibition/apoptosis.
Methods: Stable MSLN overexpressing MIA PaCa-2 cells (MIA-MSLN), stable MSLN-silenced AsPC-1 cells (AsPC-shMSLN) and other pancreatic cells (MIA-PaCa2, Panc 28, Capan-1, BxPC3, PL 45, Hs 766T, AsPC-1, Capan-2, Panc 48) were used. NF-κB activation was examined by western blots and luciferase reporter assay. TNF-α induced growth inhibition/apoptosis was measured by MTT, TUNEL assay and caspase activation. IL-6 was measured using luminex based assay.
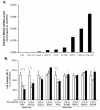
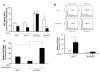
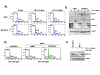
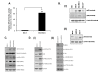
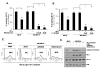
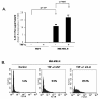
Results: Compared to low endogenous MSLN-expressing MIA PaCa-2 and Panc 28 cells, high endogenous MSLN-expressing Capan-1, BxPC3, PL 45, Hs 766T, AsPC-1, Capan-2, Panc 48 cells were resistant to TNF-α induced growth inhibition. Stable MSLN overexpressing MIA-PaCa2 cells (MIA-MSLN) were resistant to TNF-α-induced apoptosis while stable MSLN-silenced AsPC1 cells (AsPC-shMSLN) were sensitive. Interestingly, TNF-α-treated MIA-MSLN cells showed increased cell cycle progression and cyclin A induction, both of which were reversed by caspase inhibition. We further found that MIA-MSLN cells showed increased expression of anti-apoptotic Bcl-XL and Mcl-1; deactivated (p-Ser75) BAD, and activated (p-Ser70) Bcl-2. Constitutively activated NF-κB and Akt were evident in MIA-MSLN cells that could be suppressed by MSLN siRNA with a resultant increase in sensitivity of TNF-α induced apoptosis. Blocking NF-κB using IKK inhibitor wedelolactone also increased sensitivity to TNF-α-mediated cytotoxicity with concomitant decrease in Mcl-1. Blocking Akt using PI3K inhibitor also had a likewise effect presumably affecting cell cycle. MIA-MSLN cells produced increased IL-6 and were increased furthermore by TNF-α treatment. SiRNA-silencing of IL-6 increased TNF-α sensitivity of MIA-MSLN cells.
Conclusions: Our study delineates a MSLN-Akt-NF-κB-IL-6-Mcl-1 survival axis that may be operative in PC cells, and might help cancer cells' survival in the highly inflammatory milieu evident in PC. Further, for the success of TNFerade + gemcitabine to be successful, we feel the simultaneous inhibition of components of this axis is also essential.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

