Role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1alpha in AKT/PKB-mediated inhibition of hepatitis B virus biosynthesis
- PMID: 21880746
- PMCID: PMC3209318
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00832-11
Role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1alpha in AKT/PKB-mediated inhibition of hepatitis B virus biosynthesis
Abstract
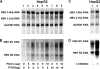
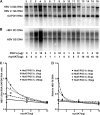
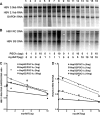
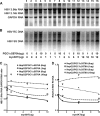
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) transcription and replication are essentially restricted to hepatocytes because liver-enriched transcription factors govern viral RNA synthesis. The level of transcription from the HBV promoters depends on both the transcription factors binding to these regulatory sequence elements and their ability to recruit coactivators capable of mediating assembly of the transcription preinitiation complex containing RNA polymerase II. Nuclear receptors are a primary determinant of HBV pregenomic RNA synthesis and, hence, viral replication. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α (PGC1α) enhances the activity of nuclear receptors and, consequently, HBV biosynthesis. PGC1α is also an important target of signal transduction pathways involved in hepatic glucose and lipid homeostasis, suggesting that this coactivator may have an important role in modulating HBV biosynthesis under various physiological conditions. Consistent with this suggestion, v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog/protein kinase B (AKT/PKB) is shown to modulate PGC1α activity and, hence, HBV transcription and replication in a cell line-specific manner. In addition, AKT can modulate HBV replication in some but not all cell lines at a posttranscriptional step in the viral life cycle. These observations demonstrate that growth and nutritional signals have the capacity to influence viral production, but the magnitude of these effects will depend on the precise cellular context in which they occur.
Figures



Similar articles
-
PGC1α Transcriptional Adaptor Function Governs Hepatitis B Virus Replication by Controlling HBcAg/p21 Protein-Mediated Capsid Formation.J Virol. 2017 Sep 27;91(20):e00790-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00790-17. Print 2017 Oct 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28768874 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma Coactivator 1alpha and small heterodimer partner differentially regulate nuclear receptor-dependent hepatitis B virus biosynthesis.J Virol. 2009 Dec;83(23):12535-44. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01623-09. Epub 2009 Sep 30. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19793822 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct regulation of hepatitis B virus biosynthesis by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1alpha and small heterodimer partner in human hepatoma cell lines.J Virol. 2009 Dec;83(23):12545-51. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01624-09. Epub 2009 Sep 30. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19793803 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding the multifaceted interventions between human sirtuin 2 and dynamic hepatitis B viral proteins to confirm their roles in HBV replication.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jan 4;13:1234903. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1234903. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38239506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Regulation of HBV Transcription and Replication.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1179:39-69. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-9151-4_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 31741333 Review.
Cited by
-
High mobility group AT-hook 1 (HMGA1) is an important positive regulator of hepatitis B virus (HBV) that is reciprocally upregulated by HBV X protein.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Feb 28;50(4):2157-2171. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac070. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35137191 Free PMC article.
-
PGC1α Transcriptional Adaptor Function Governs Hepatitis B Virus Replication by Controlling HBcAg/p21 Protein-Mediated Capsid Formation.J Virol. 2017 Sep 27;91(20):e00790-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00790-17. Print 2017 Oct 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28768874 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator family members competitively regulate hepatitis b virus biosynthesis.Virology. 2019 Jan 2;526:214-221. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2018.10.027. Epub 2018 Nov 10. Virology. 2019. PMID: 30419515 Free PMC article.
-
CRTC2 enhances HBV transcription and replication by inducing PGC1α expression.Virol J. 2014 Feb 14;11:30. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-11-30. Virol J. 2014. PMID: 24529027 Free PMC article.
-
The hepatitis B virus (HBV) HBx protein activates AKT to simultaneously regulate HBV replication and hepatocyte survival.J Virol. 2015 Jan 15;89(2):999-1012. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02440-14. Epub 2014 Oct 29. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25355887 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beasley R. P. 1988. Hepatitis B virus: the major etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 61: 1942–1956 - PubMed
-
- Beasley R. P., Hwang L.-Y., Lin C.-C., Chien C.-S. 1981. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus—a prospective study of 22707 men in Taiwan. Lancet ii: 1129–1133 - PubMed
-
- Bhaskar P. T., Hay N. 2007. The two TORCs and Akt. Dev. Cell 12: 487–502 - PubMed
-
- Boyault S., et al. 2007. Transcriptome classification of HCC is related to gene alterations and to new therapeutic targets. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 45: 42–52 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

