Accelerated age-related cognitive decline and neurodegeneration, caused by deficient DNA repair
- PMID: 21880916
- PMCID: PMC6703271
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1589-11.2011
Accelerated age-related cognitive decline and neurodegeneration, caused by deficient DNA repair
Abstract
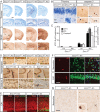
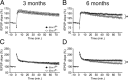
Age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases are a growing challenge for our societies with their aging populations. Accumulation of DNA damage has been proposed to contribute to these impairments, but direct proof that DNA damage results in impaired neuronal plasticity and memory is lacking. Here we take advantage of Ercc1(Δ/-) mutant mice, which are impaired in DNA nucleotide excision repair, interstrand crosslink repair, and double-strand break repair. We show that these mice exhibit an age-dependent decrease in neuronal plasticity and progressive neuronal pathology, suggestive of neurodegenerative processes. A similar phenotype is observed in mice where the mutation is restricted to excitatory forebrain neurons. Moreover, these neuron-specific mutants develop a learning impairment. Together, these results suggest a causal relationship between unrepaired, accumulating DNA damage, and age-dependent cognitive decline and neurodegeneration. Hence, accumulated DNA damage could therefore be an important factor in the onset and progression of age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
Figures



References
-
- Bach ME, Barad M, Son H, Zhuo M, Lu YF, Shih R, Mansuy I, Hawkins RD, Kandel ER. Age-related defects in spatial memory are correlated with defects in the late phase of hippocampal long-term potentiation in vitro and are attenuated by drugs that enhance the cAMP signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:5280–5285. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bergstralh DT, Sekelsky J. Interstrand crosslink repair: can XPF-ERCC1 be let off the hook? Trends Genet. 2008;24:70–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
