Kalirin binds the NR2B subunit of the NMDA receptor, altering its synaptic localization and function
- PMID: 21880917
- PMCID: PMC3172699
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3143-11.2011
Kalirin binds the NR2B subunit of the NMDA receptor, altering its synaptic localization and function
Abstract
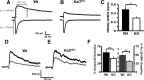
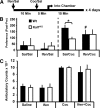
The ability of dendritic spines to change size and shape rapidly is critical in modulating synaptic strength; these morphological changes are dependent upon rearrangements of the actin cytoskeleton. Kalirin-7 (Kal7), a Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor localized to the postsynaptic density (PSD), modulates dendritic spine morphology in vitro and in vivo. Kal7 activates Rac and interacts with several PSD proteins, including PSD-95, DISC-1, AF-6, and Arf6. Mice genetically lacking Kal7 (Kal7(KO)) exhibit deficient hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP) as well as behavioral abnormalities in models of addiction and learning. Purified PSDs from Kal7(KO) mice contain diminished levels of NR2B, an NMDA receptor subunit that plays a critical role in LTP induction. Here we demonstrate that Kal7(KO) animals have decreased levels of NR2B-dependent NMDA receptor currents in cortical pyramidal neurons as well as a specific deficit in cell surface expression of NR2B. Additionally, we demonstrate that the genotypic differences in conditioned place preference and passive avoidance learning seen in Kal7(KO) mice are abrogated when animals are treated with an NR2B-specific antagonist during conditioning. Finally, we identify a stable interaction between the pleckstrin homology domain of Kal7 and the juxtamembrane region of NR2B preceding its cytosolic C-terminal domain. Binding of NR2B to a protein that modulates the actin cytoskeleton is important, as NMDA receptors require actin integrity for synaptic localization and function. These studies demonstrate a novel and functionally important interaction between the NR2B subunit of the NMDA receptor and Kalirin, proteins known to be essential for normal synaptic plasticity.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Kalirin-7 is required for synaptic structure and function.J Neurosci. 2008 Nov 19;28(47):12368-82. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4269-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19020030 Free PMC article.
-
Kalirin-7 is an essential component of both shaft and spine excitatory synapses in hippocampal interneurons.J Neurosci. 2008 Jan 16;28(3):711-24. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5283-07.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18199770 Free PMC article.
-
Casein kinase 2 regulates the NR2 subunit composition of synaptic NMDA receptors.Neuron. 2010 Sep 23;67(6):984-96. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.08.011. Neuron. 2010. PMID: 20869595 Free PMC article.
-
Kalirin-7 is a key player in the formation of excitatory synapses in hippocampal neurons.ScientificWorldJournal. 2010 Aug 17;10:1655-66. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2010.148. ScientificWorldJournal. 2010. PMID: 20730383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kalirin signaling: implications for synaptic pathology.Mol Neurobiol. 2012 Feb;45(1):109-18. doi: 10.1007/s12035-011-8223-z. Epub 2011 Dec 23. Mol Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22194219 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Striatal synaptic dysfunction and hippocampal plasticity deficits in the Hu97/18 mouse model of Huntington disease.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 11;9(4):e94562. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094562. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24728353 Free PMC article.
-
Subunit-selective N-Methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) Receptor Signaling through Brefeldin A-resistant Arf Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factors BRAG1 and BRAG2 during Synapse Maturation.J Biol Chem. 2016 Apr 22;291(17):9105-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.691717. Epub 2016 Feb 16. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26884337 Free PMC article.
-
GluN2B-mediated regulation of silent synapses for receptor specification and addiction memory.Exp Mol Med. 2025 Feb;57(2):436-449. doi: 10.1038/s12276-025-01399-z. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Exp Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39930130 Free PMC article.
-
Regulating Rac in the nervous system: molecular function and disease implication of Rac GEFs and GAPs.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:632450. doi: 10.1155/2015/632450. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25879033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Rac-GEF Tiam1 Promotes Dendrite and Synapse Stabilization of Dentate Granule Cells and Restricts Hippocampal-Dependent Memory Functions.J Neurosci. 2021 Feb 10;41(6):1191-1206. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3271-17.2020. Epub 2020 Dec 16. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33328293 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akashi K, Kakizaki T, Kamiya H, Fukaya M, Yamasaki M, Abe M, Natsume R, Watanabe M, Sakimura K. NMDA receptor GluN2B (GluR epsilon 2/NR2B) subunit is crucial for channel function, postsynaptic macromolecular organization, and actin cytoskeleton at hippocampal CA3 synapses. J Neurosci. 2009;29:10869–10882. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barria A, Malinow R. NMDA receptor subunit composition controls synaptic plasticity by regulating binding to CaMKII. Neuron. 2005;48:289–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
