Nineteen cases of Buruli ulcer diagnosed in Japan from 1980 to 2010
- PMID: 21880966
- PMCID: PMC3209082
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00783-11
Nineteen cases of Buruli ulcer diagnosed in Japan from 1980 to 2010
Abstract
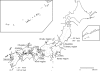
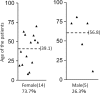
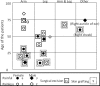
The etiology, clinical manifestations, and treatment of 19 sporadic cases of Buruli ulcer (BU) in Japan are described. The cases originated in different regions of Honshu Island, with no evidence of patient contact with an aquatic environment. The majority (73.7%) of cases occurred in females, with an average age of 39.1 years for females and 56.8 years for males. All patients developed ulcers on exposed areas of the skin (e.g., face, extremities). Most ulcers were <5 cm in diameter (category I), except in one severe progressive case (category II). Pain was absent in 10 of the 19 cases. Fourteen ulcers were surgically excised, and nine patients needed skin grafting. All cases were treated with various antibiotic regimens, with no reported recurrences as of March 2011. Mycobacterium ulcerans-specific IS2404 was detected in all cases. Ten isolates had identical 16S rRNA gene sequences, which were similar to those of M. ulcerans. However, the rpoB gene showed a closer resemblance to Mycobacterium marinum or Mycobacterium pseudoshottsii. PCR identified pMUM001 in all isolates but failed to detect one marker. DNA-DNA hybridization misidentified all isolates as M. marinum. The drug susceptibility profile of the isolates also differed from that of M. ulcerans. Sequence analysis revealed "Mycobacterium ulcerans subsp. shinshuense" as the etiologic agent of BU in Japan. Clinical manifestations were comparable to those of M. ulcerans but differed as follows: (i) cases were not concentrated in a particular area; (ii) there was no suspected connection to an aquatic environment; (iii) drug susceptibility was different; and (iv) bacteriological features were different.
Figures


References
-
- Alsop D. G. 1972. The Bairnsdale ulcer. Aust. N. Z. J. Surg. 41:317–319 - PubMed
-
- Clancey J. K., Dodge O. G., Lunn H. F., Oduori M. L. 1961. Mycobacterial skin ulcers in Uganda. Lancet ii:951–954 - PubMed
-
- Faber W. R., et al. 2000. First reported case of Mycobacterium ulcerans infection in a patient from China. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 94:277–279 - PubMed
-
- Fenner F. 1951. The significance of the incubation period in infectious diseases. Med. J. Aust. 2:813–818 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

