Basolateral LPS inhibits NHE3 and HCOFormula absorption through TLR4/MyD88-dependent ERK activation in medullary thick ascending limb
- PMID: 21881005
- PMCID: PMC3233797
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00237.2011
Basolateral LPS inhibits NHE3 and HCOFormula absorption through TLR4/MyD88-dependent ERK activation in medullary thick ascending limb
Abstract
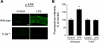
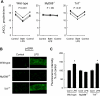
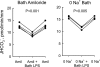
Sepsis is associated with defects in renal tubule function, but the underlying mechanisms are incompletely understood. Recently, we demonstrated that Gram-negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) inhibits HCO(3)(-) absorption in the medullary thick ascending limb (MTAL) through activation of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). Here, we examined the mechanisms responsible for inhibition of HCO(3)(-) absorption by basolateral LPS. Adding LPS to the bath decreased HCO(3)(-) absorption by 30% in rat and mouse MTALs perfused in vitro. The inhibition of HCO(3)(-) absorption was eliminated by the mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MEK)/ERK inhibitors U0126 and PD98059. LPS induced a rapid (<15 min) and sustained (up to 60 min) increase in ERK phosphorylation in microdissected MTALs that was blocked by PD98059. The effects of basolateral LPS to activate ERK and inhibit HCO(3)(-) absorption were eliminated in MTALs from TLR4(-/-) and myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88)(-/-) mice but were preserved in MTALs from TIR (Toll/interleukin-1 receptor) domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β (Trif)(-/-) mice. Basolateral LPS decreased apical Na(+)/H(+) exchanger 3 NHE3 activity through a decrease in maximal velocity (V(max)). The inhibition of NHE3 by LPS was eliminated by MEK/ERK inhibitors. LPS inhibited HCO(3)(-) absorption despite the presence of physiological stimuli that activate ERK in the MTAL. We conclude that basolateral LPS inhibits HCO(3)(-) absorption in the MTAL through activation of a TLR4/MyD88/MEK/ERK pathway coupled to inhibition of NHE3. These studies identify NHE3 as a target of TLR4 signaling in the MTAL and show that bacterial molecules can impair the absorptive functions of renal tubules through inhibition of this exchanger. The ERK pathway links TLR4 to downstream modulation of ion transport proteins and represents a potential target for treatment of sepsis-induced renal tubule dysfunction.
Figures
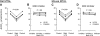



Comment in
-
Uncovering the pathway of sepsis-induced renal tubular dysfunction. Focus on "Basolateral LPS inhibits NHE3 and HCOFormula absorption through TLR4/MyD88-dependent ERK activation in medullary thick ascending limb".Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011 Dec;301(6):C1290-2. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00350.2011. Epub 2011 Sep 21. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21940669 No abstract available.
References
-
- Alexander RT, Grinstein S. Tethering, recycling and activation of the epithelial sodium-proton exchanger, NHE-3. J Exp Biol 212: 1630–1637, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Alpern RJ. Renal acidification mechanisms. In: The Kidney, edited by Brenner BM, Rector FC., Jr Philadelphia, PA: Saunders, 2000, Vol. I, p. 455–519
-
- Amemiya M, Loffing J, Lotscher M, Kaissling B, Alpern RJ, Moe OW. Expression of NHE-3 in the apical membrane of rat renal proximal tubule and thick ascending limb. Kidney Int 48: 1206–1215, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Banerjee A, Gerondakis S. Coordinating TLR-activated signaling pathways in cells of the immune system. Immunol Cell Biol 85: 420–424, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

