Therapeutic strategies for the clinical blockade of IL-6/gp130 signaling
- PMID: 21881215
- PMCID: PMC3163962
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI57158
Therapeutic strategies for the clinical blockade of IL-6/gp130 signaling
Abstract
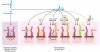
The successful treatment of certain autoimmune conditions with the humanized anti-IL-6 receptor (IL-6R) antibody tocilizumab has emphasized the clinical importance of cytokines that signal through the β-receptor subunit glycoprotein 130 (gp130). In this Review, we explore how gp130 signaling controls disease progression and examine why IL-6 has a special role among these cytokines as an inflammatory regulator. Attention will be given to the role of the soluble IL-6R, and we will provide a perspective into the clinical blockade of IL-6 activity in autoimmunity, inflammation, and cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Feldmann M. Development of anti-TNF therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2(5):364–371. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

