Clinical relevance of detection of lymphovascular invasion in primary melanoma using endothelial markers D2-40 and CD34
- PMID: 21881483
- PMCID: PMC3623282
- DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31822573f5
Clinical relevance of detection of lymphovascular invasion in primary melanoma using endothelial markers D2-40 and CD34
Abstract
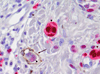
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) using endothelial markers may facilitate the detection of lymphovascular invasion (LVI) in primary melanoma; however, the clinical implications of enhanced detection are unknown. We evaluated whether the use of lymphatic endothelial marker D2-40 and panvascular marker CD34 increases LVI positivity relative to routine histology alone and then evaluated the prognostic relevance of LVI detected using these markers in terms of disease-free (DFS) and overall survival (OS). A total of 246 primary melanomas were assessed for LVI using D2-40, CD34, and routine histology. Associations between LVI positivity and clinicopathologic variables, DFS, and OS were compared using univariate and multivariate analyses. The use of endothelial markers increased the rate of LVI positivity (18% using D2-40 and/or CD34 vs. 3% by routine histology, P<0.0001). On univariate analysis, IHC-detected LVI was significantly associated with more adverse clinicopathologic variables (thickness, ulceration, mitoses, and nodular subtype) compared with LVI detected by routine histology (thickness and ulceration only). In a multivariate model controlling for stage, LVI detected using IHC markers remained a significant marker of both reduced DFS [hazard ratio (HR), 2.01; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.27-3.18; P=0.003] and OS (HR, 2.08; 95% CI: 1.25-3.46; P=0.005). Results show that D2-40 and CD34 increase the detection of LVI in primary melanoma and that cases missed by routine histology have prognostic relevance.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have disclosed that they have no significant relationships with, or financial interest in, any commercial companies pertaining to this article.
Figures


References
-
- Bolenz C, Herrmann E, Bastian PJ, et al. Lymphovascular invasion is an independent predictor of oncological outcomes in patients with lymph node-negative urothelial bladder cancer treated by radical cystectomy: a multicentre validation trial. BJU Int. 2010;106:493–499. - PubMed
-
- Dadras SS, Lange-Asschenfeldt B, Velasco P, et al. Tumor lymphangiogenesis predicts melanoma metastasis to sentinel lymph nodes. Mod Pathol. 2005;18:1232–1242. - PubMed
-
- Doeden K, Ma Z, Narasimhan B, et al. Lymphatic invasion in cutaneous melanoma is associated with sentinel lymph node metastasis. J Cutan Pathol. 2009;36:772–780. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

