The autoimmune concept of atherosclerosis
- PMID: 21881502
- PMCID: PMC3216126
- DOI: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e32834aa0c2
The autoimmune concept of atherosclerosis
Abstract
Purpose of review: This review summarizes the recent data on the 'Autoimmune Concept of Atherosclerosis', according to which the first stage of this disease is due to an autoimmune reaction against arterial endothelial cells expressing heat shock protein 60 (HSP60) and adhesion molecules when stressed by classical atherosclerosis risk factors. Special emphasis is put on oxidized low-density lipoproteins as early endothelial stressors.
Recent findings: Plasma cholesterol and LDL levels considered 'normal' by the medical community are possibly too high from an evolutionary viewpoint. The proinflammatory milieu at sites of early atherosclerotic lesions could be conducive to oxidation of LDL in situ. LDL oxidation can also take place at nonvascular sites or in the circulation under general proinflammatory conditions explaining its proatherosclerotic role in 'normocholesterolemic' individuals.
Summary: We hypothesize that the plasma cholesterol and LDL levels currently considered normal are evolutionarily too high. Cholesterol and/or oxidized low-density lipoprotein, even as a mild HSP60-inducing endothelial stressor, function as a ubiquitous risk factor. If this hypothesis is true, most members of developed societies might be at risk to develop atherosclerotic plaques at anti-HSP60-immunity-triggered intimal inflammatory foci, irrespective of the primary risk-factor(s).
Figures
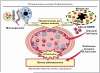
 , HSP60;
, HSP60;  , altered HSP60;
, altered HSP60;  , cell-specific proteins;
, cell-specific proteins;  , adhesion molecules;
, adhesion molecules;  , T cell;
, T cell;  , anti-hHSP60 antibody. Partly adapted from Servier Medical Art.
, anti-hHSP60 antibody. Partly adapted from Servier Medical Art.

References
-
- Xu QB, Oberhuber G, Gruschwitz M, Wick G. Immunology of atherosclerosis: cellular composition and major histocompatibility complex class II antigen expression in aortic intima, fatty streaks, and atherosclerotic plaques in young and aged human specimens. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990;56:344–359. - PubMed
-
- Millonig G, Malcom GT, Wick G. Early inflammatory-immunological lesions in juvenile atherosclerosis from the Pathobiological Determinants of Atherosclerosis in Youth (PDAY)-study. Atherosclerosis. 2002;160:441–448. - PubMed
-
- Millonig G, Niederegger H, Rabl W, et al. Network of vascular-associated dendritic cells in intima of healthy young individuals. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2001;21:503–508. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

