The development of N-α-(2-carboxyl)benzoyl-N(5)-(2-fluoro-1-iminoethyl)-l-ornithine amide (o-F-amidine) and N-α-(2-carboxyl)benzoyl-N(5)-(2-chloro-1-iminoethyl)-l-ornithine amide (o-Cl-amidine) as second generation protein arginine deiminase (PAD) inhibitors
- PMID: 21882827
- PMCID: PMC3196593
- DOI: 10.1021/jm2008985
The development of N-α-(2-carboxyl)benzoyl-N(5)-(2-fluoro-1-iminoethyl)-l-ornithine amide (o-F-amidine) and N-α-(2-carboxyl)benzoyl-N(5)-(2-chloro-1-iminoethyl)-l-ornithine amide (o-Cl-amidine) as second generation protein arginine deiminase (PAD) inhibitors
Erratum in
- J Med Chem. 2011 Nov 24;54(22):7942
Abstract
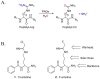
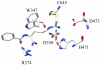
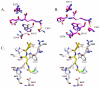
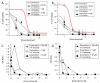
Protein arginine deiminase (PAD) activity is upregulated in a number of human diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis, and cancer. These enzymes, there are five in humans (PADs 1-4 and 6), regulate gene transcription, cellular differentiation, and the innate immune response. Building on our successful generation of F- and Cl-amidine, which irreversibly inhibit all of the PADs, a structure-activity relationship was performed to develop second generation compounds with improved potency and selectivity. Incorporation of a carboxylate ortho to the backbone amide resulted in the identification of N-α-(2-carboxyl)benzoyl-N(5)-(2-fluoro-1-iminoethyl)-l-ornithine amide (o-F-amidine) and N-α-(2-carboxyl)benzoyl-N(5)-(2-chloro-1-iminoethyl)-l-ornithine amide (o-Cl-amidine), as PAD inactivators with improved potency (up to 65-fold) and selectivity (up to 25-fold). Relative to F- and Cl-amidine, the compounds also show enhanced potency in cellulo. As such, these compounds will be versatile chemical probes of PAD function.
Figures



References
-
- Kearney PL, Bhatia M, Jones NG, Luo Y, Glascock MC, Catchings KL, Yamada M, Thompson PR. Kinetic characterization of protein arginine deiminase 4: a transcriptional corepressor implicated in the onset and progression of rheumatoid arthritis. Biochemistry. 2005;44:10570–10582. - PubMed
-
- Vossenaar ER, Zendman AJ, van Venrooij WJ, Pruijn GJ. PAD, a growing family of citrullinating enzymes: genes, features and involvement in disease. Bioessays. 2003;25:1106–1118. - PubMed
-
- Raijmakers R, Zendman AJ, Egberts WV, Vossenaar ER, Raats J, Soede-Huijbregts C, Rutjes FP, van Veelen PA, Drijfhout JW, Pruijn GJ. Methylation of arginine residues interferes with citrullination by peptidylarginine deiminases in vitro. J Mol Biol. 2007;367:1118–1129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

