Structure-activity relationships of vanilloid receptor agonists for arteriolar TRPV1
- PMID: 21883148
- PMCID: PMC3372831
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01645.x
Structure-activity relationships of vanilloid receptor agonists for arteriolar TRPV1
Abstract
Background and purpose: The transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) plays a role in the activation of sensory neurons by various painful stimuli and is a therapeutic target. However, functional TRPV1 that affect microvascular diameter are also expressed in peripheral arteries and we attempted to characterize this receptor.
Experimental approach: Sensory TRPV1 activation was measured in rats by use of an eye wiping assay. Arteriolar TRPV1-mediated smooth muscle specific responses (arteriolar diameter, changes in intracellular Ca(2+)) were determined in isolated, pressurized skeletal muscle arterioles obtained from the rat and wild-type or TRPV1(-/-) mice and in canine isolated smooth muscle cells. The vascular pharmacology of the TRPV1 agonists (potency, efficacy, kinetics of action and receptor desensitization) was determined in rat isolated skeletal muscle arteries.
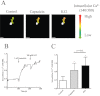
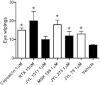
Key results: Capsaicin evoked a constrictor response in isolated arteries similar to that mediated by noradrenaline, this was absent in arteries from TRPV1 knockout mice and competitively inhibited by TRPV1 antagonist AMG9810. Capsaicin increased intracellular Ca(2+) in the arteriolar wall and in isolated smooth muscle cells. The TRPV1 agonists evoked similar vascular constrictions (MSK-195 and JYL-79) or were without effect (resiniferatoxin and JYL-273), although all increased the number of responses (sensory activation) in the eye wiping assay. Maximal doses of all agonists induced complete desensitization (tachyphylaxis) of arteriolar TRPV1 (with the exception of capsaicin). Responses to the partial agonist JYL-1511 suggested 10% TRPV1 activation is sufficient to evoke vascular tachyphylaxis without sensory activation.
Conclusions and implications: Arteriolar TRPV1 have different pharmacological properties from those located on sensory neurons in the rat.
© 2011 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

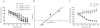





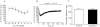


Similar articles
-
Different desensitization patterns for sensory and vascular TRPV1 populations in the rat: expression, localization and functional consequences.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 8;8(11):e78184. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078184. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24250792 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation-dependent desensitization by anandamide of vanilloid receptor-1 (TRPV1) function in rat skeletal muscle arterioles and in Chinese hamster ovary cells expressing TRPV1.Mol Pharmacol. 2006 Mar;69(3):1015-23. doi: 10.1124/mol.105.015644. Epub 2005 Dec 7. Mol Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16338989
-
TRPV1 expressed throughout the arterial circulation regulates vasoconstriction and blood pressure.J Physiol. 2020 Dec;598(24):5639-5659. doi: 10.1113/JP279909. Epub 2020 Oct 6. J Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32944976 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacology of the capsaicin receptor, transient receptor potential vanilloid type-1 ion channel.Prog Drug Res. 2014;68:39-76. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-0828-6_2. Prog Drug Res. 2014. PMID: 24941664 Review.
-
Complex Regulation of TRPV1 by Vanilloids.In: Liedtke WB, Heller S, editors. TRP Ion Channel Function in Sensory Transduction and Cellular Signaling Cascades. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2007. Chapter 6. In: Liedtke WB, Heller S, editors. TRP Ion Channel Function in Sensory Transduction and Cellular Signaling Cascades. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2007. Chapter 6. PMID: 21204495 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
The TFOS International Workshop on Contact Lens Discomfort: report of the subcommittee on neurobiology.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013 Oct 18;54(11):TFOS71-97. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-13226. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013. PMID: 24058137 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloperoxidase evokes substantial vasomotor responses in isolated skeletal muscle arterioles of the rat.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2015 May;214(1):109-23. doi: 10.1111/apha.12488. Epub 2015 Mar 28. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2015. PMID: 25760778 Free PMC article.
-
Automated detection and measurement of isolated retinal arterioles by a combination of edge enhancement and cost analysis.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 13;9(3):e91791. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091791. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24626349 Free PMC article.
-
Glycogen phosphorylase inhibition improves beta cell function.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Jan;175(2):301-319. doi: 10.1111/bph.13819. Epub 2017 Jun 18. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28409826 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond Neuronal Heat Sensing: Diversity of TRPV1 Heat-Capsaicin Receptor-Channel Functions.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Feb 5;14:612480. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.612480. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33613196 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bhave G, Zhu W, Wang H, Brasier DJ, Oxford GS, Gereau R. cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulates desensitization of the capsaicin receptor (VR1) by direct phosphorylation. Neuron. 2002;35:721–731. - PubMed
-
- Caterina MJ, Schumacher MA, Tominaga M, Rosen TA, Levine JD, Julius D. The capsaicin receptor: a heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature. 1997;389:816–824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

