Sotrastaurin, a protein kinase C inhibitor, ameliorates ischemia and reperfusion injury in rat orthotopic liver transplantation
- PMID: 21883905
- PMCID: PMC3625141
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2011.03700.x
Sotrastaurin, a protein kinase C inhibitor, ameliorates ischemia and reperfusion injury in rat orthotopic liver transplantation
Abstract
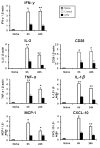
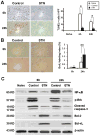
Sotraustaurin (STN), a small molecule, targeted protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor that prevents T-lymphocyte activation via a calcineurin-independent pathway, is currently being tested in Phase II renal and liver transplantation clinical trials. We have documented the key role of activated T cells in the inflammation cascade leading to liver ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI). This study explores putative cytoprotective functions of STN in a clinically relevant rat model of hepatic cold ischemia followed by orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT). Livers from Sprague-Dawley rats were stored for 30 h at 4°C in UW solution, and then transplanted to syngeneic recipients. STN treatment of liver donors/recipients or recipients only prolonged OLT survival to >90% (vs. 40% in controls), decreased hepatocellular damage and improved histological features of IRI. STN treatment decreased activation of T cells, and diminished macrophage/neutrophil accumulation in OLTs. These beneficial effects were accompanied by diminished apoptosis, NF-κB/ERK signaling, depressed proapoptotic cleaved caspase-3, yet upregulated antiapoptotic Bcl-2/Bcl-xl and hepatic cell proliferation. In vitro, STN decreased PKCθ/IκBα activation and IL-2/IFN-γ production in ConA-stimulated spleen T cells, and diminished TNF-α/IL-1β in macrophage-T cell cocultures. This study documents positive effects of STN on liver IRI in OLT rat model that may translate as an additional benefit of STN in clinical liver transplantation.
©2011 The Authors Journal compilation © 2011 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript have no conflicts of interest to disclose, as described by the American Journal of Transplantation.
Figures



References
-
- Evenou JP, Wagner J, Zenke G, Brinkmann V, Wagner K, Kovarik J, et al. The potent protein kinase C-selective inhibitor AEB071 (sotrastaurin) represents a new class of immunosuppressive agents affecting early T-cell activation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009;330(3):792–801. - PubMed
-
- Matz M, Naik M, Mashreghi MF, Glander P, Neumayer HH, Budde K. Evaluation of the novel protein kinase C inhibitor sotrastaurin as immunosuppressive therapy after renal transplantation. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2011;7(1):103–113. - PubMed
-
- Weckbecker G, Pally C, Beerli C, Burkhart C, Wieczorek G, Metzler B, et al. Effects of the novel protein kinase C inhibitor AEB071 (Sotrastaurin) on rat cardiac allograft survival using single agent treatment or combination therapy with cyclosporine, everolimus or FTY720. Transpl Int. 2010;23(5):543–552. - PubMed
-
- Fang YH, Joo DJ, Lim BJ, Kim JY, Kim MS, Jeong HJ, et al. AEB-071 Versus Tacrolimus Monotherapy to Prevent Acute Cardiac Allograft Rejection in the Rat: A Preliminary Report. Transplant Proc. 2010;42(3):976–979. - PubMed
-
- Wagner J, Evenou JP, Zenke G, Brinkmann V, Pally C, Bigaud M, et al. The first-in-class oral protein kinase C inhibitor AEB071 prolongs renal allograft survival in nonhuman primates and suppresses lymphocyte proliferation at safe exposures in human proof-of-concept studies [abstract] Transplant. 2006;82(S3):86.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

