β1 integrin mediates an alternative survival pathway in breast cancer cells resistant to lapatinib
- PMID: 21884573
- PMCID: PMC3236347
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr2936
β1 integrin mediates an alternative survival pathway in breast cancer cells resistant to lapatinib
Abstract
Introduction: The overexpression of human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER)-2 in 20% of human breast cancers and its association with aggressive growth has led to widespread use of HER2-targeted therapies, such as trastuzumab (T) and lapatinib (L). Despite the success of these drugs, their efficacy is limited in patients whose tumors demonstrate de novo or acquired resistance to treatment. The β1 integrin resides on the membrane of the breast cancer cell, activating several elements of breast tumor progression including proliferation and survival.
Methods: We developed a panel of HER2-overexpressing cell lines resistant to L, T, and the potent LT combination through long-term exposure and validated these models in 3D culture. Parental and L/T/LT-resistant cells were subject to HER2 and β1 integrin inhibitors in 3D and monitored for 12 days, followed by quantification of colony number. Parallel experiments were conducted where cells were either stained for Ki-67 and Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) or harvested for protein and analyzed by immunoblot. Results were subjected to statistical testing using analysis of variance and linear contrasts, followed by adjustment with the Sidak method.
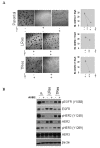
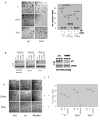
Results: Using multiple cell lines including BT474 and HCC1954, we reveal that in L and LT resistance, where phosphorylation of EGFR/HER1, HER2, and HER3 are strongly inhibited, kinases downstream of β1 integrin--including focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and Src--are up-regulated. Blockade of β1 by the antibody AIIB2 abrogates this up-regulation and functionally achieves significant growth inhibition of L and LT resistant cells in 3D, without dramatically affecting the parental cells. SiRNA against β1 as well as pharmacologic inhibition of FAK achieve the same growth inhibitory effect. In contrast, trastuzumab-resistant cells, which retain high levels of phosphorylated EGFR/HER1, HER2, and HER3, are only modestly growth-inhibited by AIIB2.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that HER2 activity, which is suppressed in resistance involving L but not T alone, dictates whether β1 mediates an alternative pathway driving resistance. Our findings justify clinical studies investigating the inhibition of β1 or its downstream signaling moieties as strategies to overcome acquired L and LT resistance.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Different mechanisms for resistance to trastuzumab versus lapatinib in HER2-positive breast cancers--role of estrogen receptor and HER2 reactivation.Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13(6):R121. doi: 10.1186/bcr3067. Epub 2011 Nov 28. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 22123186 Free PMC article.
-
An heregulin-EGFR-HER3 autocrine signaling axis can mediate acquired lapatinib resistance in HER2+ breast cancer models.Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(5):R85. doi: 10.1186/bcr3480. Breast Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24044505 Free PMC article.
-
Dacomitinib (PF-00299804), an irreversible Pan-HER inhibitor, inhibits proliferation of HER2-amplified breast cancer cell lines resistant to trastuzumab and lapatinib.Mol Cancer Ther. 2012 Sep;11(9):1978-87. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0730. Epub 2012 Jul 3. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012. PMID: 22761403
-
Lapatinib.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2018;211:19-44. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-91442-8_2. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30069757 Review.
-
Overcoming treatment resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer: potential strategies.Drugs. 2012 Jun 18;72(9):1175-93. doi: 10.2165/11634000-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22686613 Review.
Cited by
-
Modeling and analysis of Hi-C data by HiSIF identifies characteristic promoter-distal loops.Genome Med. 2020 Aug 12;12(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s13073-020-00769-8. Genome Med. 2020. PMID: 32787954 Free PMC article.
-
β1 Integrin as a Prognostic and Predictive Marker in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Aug 31;17(9):1432. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091432. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27589736 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of GPCR drugs for repurposing in breast cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 6;13:1049640. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1049640. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36561339 Free PMC article.
-
Survival of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Cells: Receptor Signaling to Apoptotic Control Centers.Genes Cancer. 2013 May;4(5-6):187-95. doi: 10.1177/1947601913488598. Genes Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24069506 Free PMC article.
-
Feedback activation of STAT3 mediates trastuzumab resistance via upregulation of MUC1 and MUC4 expression.Oncotarget. 2014 Sep 30;5(18):8317-29. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2135. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25327561 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yarden Y. Biology of HER2 and its importance in breast cancer. Oncology. 2001;61(Suppl 2):1–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

