Characterization of a caleosin expressed during olive (Olea europaea L.) pollen ontogeny
- PMID: 21884593
- PMCID: PMC3180362
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-11-122
Characterization of a caleosin expressed during olive (Olea europaea L.) pollen ontogeny
Abstract
Background: The olive tree is an oil-storing species, with pollen being the second most active site in storage lipid biosynthesis. Caleosins are proteins involved in storage lipid mobilization during seed germination. Despite the existence of different lipidic structures in the anther, there are no data regarding the presence of caleosins in this organ to date. The purpose of the present work was to characterize a caleosin expressed in the olive anther over different key stages of pollen ontogeny, as a first approach to unravel its biological function in reproduction.
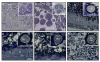
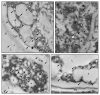
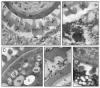
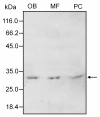
Results: A 30 kDa caleosin was identified in the anther tissues by Western blot analysis. Using fluorescence and transmission electron microscopic immunolocalization methods, the protein was first localized in the tapetal cells at the free microspore stage. Caleosins were released to the anther locule and further deposited onto the sculptures of the pollen exine. As anthers developed, tapetal cells showed the presence of structures constituted by caleosin-containing lipid droplets closely packed and enclosed by ER-derived cisternae and vesicles. After tapetal cells lost their integrity, the caleosin-containing remnants of the tapetum filled the cavities of the mature pollen exine, forming the pollen coat. In developing microspores, this caleosin was initially detected on the exine sculptures. During pollen maturation, caleosin levels progressively increased in the vegetative cell, concurrently with the number of oil bodies. The olive pollen caleosin was able to bind calcium in vitro. Moreover, PEGylation experiments supported the structural conformation model suggested for caleosins from seed oil bodies.
Conclusions: In the olive anther, a caleosin is expressed in both the tapetal and germ line cells, with its synthesis independently regulated. The pollen oil body-associated caleosin is synthesized by the vegetative cell, whereas the protein located on the pollen exine and its coating has a sporophytic origin. The biological significance of the caleosin in the reproductive process in species possessing lipid-storing pollen might depend on its subcellular emplacement. The pollen inner caleosin may be involved in OB biogenesis during pollen maturation. The protein located on the outside might rather play a function in pollen-stigma interaction during pollen hydration and germination.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The Pollen Coat Proteome: At the Cutting Edge of Plant Reproduction.Proteomes. 2016 Jan 29;4(1):5. doi: 10.3390/proteomes4010005. Proteomes. 2016. PMID: 28248215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and localization of a caleosin in olive (Olea europaea L.) pollen during in vitro germination.J Exp Bot. 2010 Mar;61(5):1537-46. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq022. Epub 2010 Feb 17. J Exp Bot. 2010. PMID: 20164143 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular localization and levels of pectins and arabinogalactan proteins in olive (Olea europaea L.) pistil tissues during development: implications for pollen-pistil interaction.Planta. 2013 Jan;237(1):305-19. doi: 10.1007/s00425-012-1774-z. Epub 2012 Oct 13. Planta. 2013. PMID: 23065053
-
ABCG15 encodes an ABC transporter protein, and is essential for post-meiotic anther and pollen exine development in rice.Plant Cell Physiol. 2013 Jan;54(1):138-54. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcs162. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23220695
-
Biogenesis and functions of lipid droplets in plants: Thematic Review Series: Lipid Droplet Synthesis and Metabolism: from Yeast to Man.J Lipid Res. 2012 Feb;53(2):215-26. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R021436. Epub 2011 Nov 1. J Lipid Res. 2012. PMID: 22045929 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Calcium-binding protein TgpCaBP regulates calcium storage of the zoonotic parasite Toxoplasma gondii.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Oct 3;12(10):e0066124. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00661-24. Epub 2024 Aug 20. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 39162521 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Triacylglycerol in Plant Stress Response.Plants (Basel). 2020 Apr 8;9(4):472. doi: 10.3390/plants9040472. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32276473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Comparison of Cysteine Proteases in the Pollen Coat and Other Tissues in Maize.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Sep 23;12:709534. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.709534. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34630461 Free PMC article.
-
The Pollen Coat Proteome: At the Cutting Edge of Plant Reproduction.Proteomes. 2016 Jan 29;4(1):5. doi: 10.3390/proteomes4010005. Proteomes. 2016. PMID: 28248215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative genomics of the lipid-body-membrane proteins oleosin, caleosin and steroleosin in magnoliophyte, lycophyte and bryophyte.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2012 Dec;10(6):345-53. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2012.08.006. Epub 2012 Dec 7. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 23317702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hesse M, Pacini E, Willemse M. The tapetum: cytology, function, biochemistry and evolution. New York: Springer-Verlag; 1993.
-
- Clément C, Laporte P, Audran JC. The loculus content during pollen development in Lilium. Sex Plant Reprod. 1998;11:94–106. doi: 10.1007/s004970050125. - DOI
-
- Steiglitz H. Role of β-1,3-glucanase in postmeiotic microspore release. Dev Biol. 1997;57:87–97. - PubMed
-
- Pacini E. Types and meaning of pollen carbohydrate reserves. Sex Plant Reprod. 1996;9:362–366. doi: 10.1007/BF02441957. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

