Viscoelastic and biological performance of low-modulus, reactive calcium phosphate-filled, degradable, polymeric bone adhesives
- PMID: 21884829
- PMCID: PMC3657135
- DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2011.08.008
Viscoelastic and biological performance of low-modulus, reactive calcium phosphate-filled, degradable, polymeric bone adhesives
Abstract
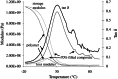
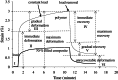
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of reactive mono- and tricalcium phosphate addition on the mechanical, surface free energy, degradation and cell compatibility properties of poly(lactide-co-propylene glycol-co-lactide) dimethacrylate (PPGLDMA) thin films. Dry composites containing up to 70 wt.% filler were in a flexible rubber state at body temperature. Filler addition increased the initial strength and Young's modulus and reduced the elastic and permanent deformation under load. The polymer had high polar surface free energy, which might enable greater spread upon bone. This was significantly reduced by filler addition but not by water immersion for 7 days. The samples exhibited reduced water sorption and associated bulk degradation when compared with previous work with thicker samples. Their cell compatibility was also improved. Filler raised water sorption and degradation but improved cell proliferation. The materials are promising bone adhesive candidates for low-load-bearing areas.
Copyright © 2011 Acta Materialia Inc. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Taljanovic M.S., Jones M.D., Ruth J.T., Sheppard J.E., Hunter T.B. Fracture fixation. Radiographics. 2003;23:1569–1590. - PubMed
-
- Meechan J.G., McCabe J.F., Beynon A.D. Adhesion of composite resin to bone—a pilot study. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1994;32:91–93. - PubMed
-
- Kennady M.C., Tucker M.R., Lester G.E., Buckley M.J. Stress shielding effect of rigid fixation plates on mandibular bone grafts: a photon absorption densitometry and quantitative computerized tomographic evaluation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1989;18:307–310. - PubMed
-
- Yuehuei H. An internal fixation in osteoporotic bone. Thieme; 2002. p. 108.
-
- Haers P.E., Suuronen R., Lindqvist C., Sailer H. Biodegradable polylactide plates and screws in orthognathic surgery: technical note. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 1998;26:87–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

