AKT/FOXO signaling enforces reversible differentiation blockade in myeloid leukemias
- PMID: 21884932
- PMCID: PMC3826540
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.032
AKT/FOXO signaling enforces reversible differentiation blockade in myeloid leukemias
Erratum in
- Cell. 2011 Sep 30;147(1):247. Schöll, Claudia [corrected to Scholl, Claudia]
Abstract
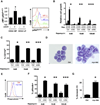
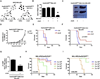
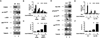
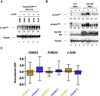
AKT activation is associated with many malignancies, where AKT acts, in part, by inhibiting FOXO tumor suppressors. We show a converse role for AKT/FOXOs in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Rather than decreased FOXO activity, we observed that FOXOs are active in ∼40% of AML patient samples regardless of genetic subtype. We also observe this activity in human MLL-AF9 leukemia allele-induced AML in mice, where either activation of Akt or compound deletion of FoxO1/3/4 reduced leukemic cell growth, with the latter markedly diminishing leukemia-initiating cell (LIC) function in vivo and improving animal survival. FOXO inhibition resulted in myeloid maturation and subsequent AML cell death. FOXO activation inversely correlated with JNK/c-JUN signaling, and leukemic cells resistant to FOXO inhibition responded to JNK inhibition. These data reveal a molecular role for AKT/FOXO and JNK/c-JUN in maintaining a differentiation blockade that can be targeted to inhibit leukemias with a range of genetic lesions.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
A new FOXO pathway required for leukemogenesis.Cell. 2011 Sep 2;146(5):669-70. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.019. Cell. 2011. PMID: 21884926
References
-
- Altomare DA, Testa JR. Perturbations of the AKT signaling pathway in human cancer. Oncogene. 2005;24:7455–7464. - PubMed
-
- Arden KC. Multiple roles of FOXO transcription factors in mammalian cells point to multiple roles in cancer. Exp. Gerontol. 2006;41:709–717. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong SA, Golub TR, Korsmeyer SJ. MLL-rearranged leukemias: insightsfrom gene expression profiling. Semin. Hematol. 2003;40:268–273. - PubMed
-
- Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell. 1999;96:857–868. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA140575/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL097748/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL100402/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA140575/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL100402/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL097794/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL097794/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL097748/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK050234/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007623/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL100402/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32HL007623-24/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA141508/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA141508/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK050234/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

