Lung tumor-associated osteoblast-derived bone morphogenetic protein-2 increased epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of cancer by Runx2/Snail signaling pathway
- PMID: 21885439
- PMCID: PMC3199481
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.256156
Lung tumor-associated osteoblast-derived bone morphogenetic protein-2 increased epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of cancer by Runx2/Snail signaling pathway
Abstract
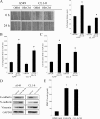
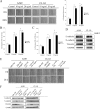
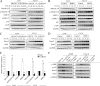
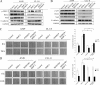
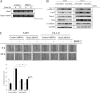
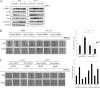
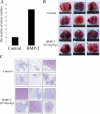
Bone is a frequent target of lung cancer metastasis and is associated with significant morbidity and a dismal prognosis. Interaction between cancer cells and the bone microenvironment causes a vicious cycle of tumor progression and bone destruction. This study analyzed the soluble factors secreted by lung tumor-associated osteoblast (TAOB), which are responsible for increasing cancer progression. The addition of bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2), present in large amounts in TAOB conditioned medium (TAOB-CM) and lung cancer patient sera, mimicked the inductive effect of TAOB-CM on lung cancer migration, invasion, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. In contrast, inhibition of BMP by noggin decreases the inductive properties of TAOB-CM and lung cancer patient sera on cancer progression. Induction of lung cancer migration by BMP-2 is associated with increased ERK and p38 activation and the up-regulation of Runx2 and Snail. Blocking ERK and p38 by a specific inhibitor significantly decreases cancer cell migration by inhibiting Runx2 up-regulation and subsequently attenuating the expression of Snail. Enhancement of Runx2 facilitates Rux2 to recruit p300, which in turn enhances histone acetylation, increases Snail expression, and decreases E-cadherin. Furthermore, inhibiting Runx2 by siRNA also suppresses BMP-2-induced Snail up-regulation and cell migration. Our findings provide novel evidence that inhibition of BMP-2 or BMP-2-mediated MAPK/Runx2/Snail signaling is an attractive therapeutic target for osteolytic bone metastases in lung cancer patients.
Figures


References
-
- Roodman G. D. (2004) N. Engl. J. Med. 350, 1655–1664 - PubMed
-
- Rosen L. S., Gordon D., Tchekmedyian S., Yanagihara R., Hirsh V., Krzakowski M., Pawlicki M., de Souza P., Zheng M., Urbanowitz G., Reitsma D., Seaman J. J. (2003) J. Clin. Oncol. 21, 3150–3157 - PubMed
-
- Kvale P. A., Simoff M., Prakash U. B. (2003) Chest 123, (Suppl. 1) 284S–311S - PubMed
-
- Onishi T., Hayashi N., Theriault R. L., Hortobagyi G. N., Ueno N. T. (2010) Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 7, 641–651 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

