Serum bicarbonate and mortality in stage 3 and stage 4 chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 21885787
- PMCID: PMC3359558
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.03730411
Serum bicarbonate and mortality in stage 3 and stage 4 chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Background and objectives: The incidence and prevalence of metabolic acidosis increase with declining kidney function. We studied the associations of both low and high serum bicarbonate levels with all-cause mortality among stage 3 and 4 chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients.
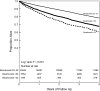
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: We examined factors associated with low (<23 mmol/L) and high (>32 mmol/L) serum bicarbonate levels using logistic regression models and associations between bicarbonate and all-cause mortality using Cox-proportional hazard models, Kaplan-Meier survival curves, and time-dependent analysis.
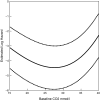
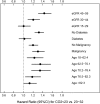
Results: Out of 41,749 patients, 13.9% (n = 5796) had low and 1.6% (n = 652) had high serum bicarbonate levels. After adjusting for relevant covariates, there was a significant association between low serum bicarbonate and all-cause mortality (hazard ratio [HR] 1.23, 95% CI 1.16, 1.31). This association was not statistically significant among patients with stage 4 CKD and diabetes. The time-dependent analysis demonstrated a significant mortality risk associated with a decline from normal to low bicarbonate level (HR 1.59, 95% CI 1.49, 1.69). High serum bicarbonate levels were associated with death irrespective of the level of kidney function (HR 1.74, 95% CI 1.52, 2.00). When serum bicarbonate was examined as a continuous variable, a J-shaped relationship was noted between serum bicarbonate and mortality.
Conclusions: Low serum bicarbonate levels are associated with increased mortality among stage 3 CKD patients and patients without diabetes. High serum bicarbonate levels are associated with mortality in both stage 3 and stage 4 CKD patients.
Figures
References
-
- Kraut JA, Kurtz I: Metabolic acidosis of CKD: Diagnosis, clinical characteristics, and treatment. Am J Kidney Dis 45: 978–993, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Domrongkitchaiporn S, Pongskul C, Sirikulchayanonta V, Stitchantrakul W, Leeprasert V, Ongphiphadhanakul B, Radinahamed P, Rajatanavin R: Bone histology and bone mineral density after correction of acidosis in distal renal tubular acidosis. Kidney Int 62: 2160–2166, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Mitch WE, Price SR: Mechanisms activated by kidney disease and the loss of muscle mass. Am J Kidney Dis 38: 1337–1342, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

