Classroom-based science research at the introductory level: changes in career choices and attitude
- PMID: 21885824
- PMCID: PMC3164567
- DOI: 10.1187/cbe.10-12-0151
Classroom-based science research at the introductory level: changes in career choices and attitude
Abstract
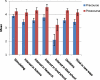
Our study, focused on classroom-based research at the introductory level and using the Phage Genomics course as the model, shows evidence that first-year students doing research learn the process of science as well as how scientists practice science. A preliminary but notable outcome of our work, which is based on a small sample, is the change in student interest in considering different career choices such as graduate education and science in general. This is particularly notable, as previous research has described research internships as clarifying or confirming rather than changing undergraduates' decisions to pursue graduate education. We hypothesize that our results differ from previous studies of the impact of engaging in research because the students in our study are still in the early stages of their undergraduate careers. Our work builds upon the classroom-based research movement and should be viewed as encouraging to the Vision and Change in Undergraduate Biology Education movement advocated by the American Association for the Advancement of Science, the National Science Foundation, and other undergraduate education stakeholders.
Figures
References
-
- Anfara VA, Brown KM, Mangione TL. Qualitative analysis on stage: making the research process more public. Educ Res. 2002;31:28–38.
-
- Brodl MR. Tapping recent alumni for the development of cutting-edge, investigative teaching lab experiments. Bioscene. J Biol College Teach. 2005;31:13–20.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

