Mechanisms of control of the free Ca2+ concentration in the endoplasmic reticulum of mouse pancreatic β-cells: interplay with cell metabolism and [Ca2+]c and role of SERCA2b and SERCA3
- PMID: 21885870
- PMCID: PMC3178295
- DOI: 10.2337/db10-1543
Mechanisms of control of the free Ca2+ concentration in the endoplasmic reticulum of mouse pancreatic β-cells: interplay with cell metabolism and [Ca2+]c and role of SERCA2b and SERCA3
Abstract
Objective: Sarco-endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase 2b (SERCA2b) and SERCA3 pump Ca(2+) in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of pancreatic β-cells. We studied their role in the control of the free ER Ca(2+) concentration ([Ca(2+)](ER)) and the role of SERCA3 in the control of insulin secretion and ER stress.
Research design and methods: β-Cell [Ca(2+)](ER) of SERCA3(+/+) and SERCA3(-/-) mice was monitored with an adenovirus encoding the low Ca(2+)-affinity sensor D4 addressed to the ER (D4ER) under the control of the insulin promoter. Free cytosolic Ca(2+) concentration ([Ca(2+)](c)) and [Ca(2+)](ER) were simultaneously recorded. Insulin secretion and mRNA levels of ER stress genes were studied.
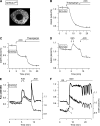
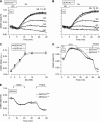
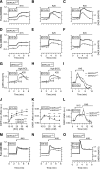
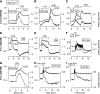
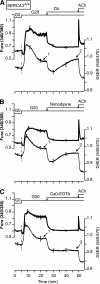
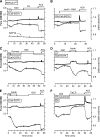
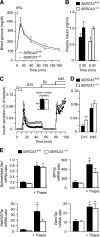
Results: Glucose elicited synchronized [Ca(2+)](ER) and [Ca(2+)](c) oscillations. [Ca(2+)](ER) oscillations were smaller in SERCA3(-/-) than in SERCA3(+/+) β-cells. Stimulating cell metabolism with various [glucose] in the presence of diazoxide induced a similar dose-dependent [Ca(2+)](ER) rise in SERCA3(+/+) and SERCA3(-/-) β-cells. In a Ca(2+)-free medium, glucose moderately raised [Ca(2+)](ER) from a highly buffered cytosolic Ca(2+) pool. Increasing [Ca(2+)](c) with high [K] elicited a [Ca(2+)](ER) rise that was larger but more transient in SERCA3(+/+) than SERCA3(-/-) β-cells because of the activation of a Ca(2+) release from the ER in SERCA3(+/+) β-cells. Glucose-induced insulin release was larger in SERCA3(-/-) than SERCA3(+/+) islets. SERCA3 ablation did not induce ER stress.
Conclusions: [Ca(2+)](c) and [Ca(2+)](ER) oscillate in phase in response to glucose. Upon [Ca(2+)](c) increase, Ca(2+) is taken up by SERCA2b and SERCA3. Strong Ca(2+) influx triggers a Ca(2+) release from the ER that depends on SERCA3. SERCA3 deficiency neither impairs Ca(2+) uptake by the ER upon cell metabolism acceleration and insulin release nor induces ER stress.
Figures

References
-
- Gilon P, Henquin JC. Influence of membrane potential changes on cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration in an electrically excitable cell, the insulin-secreting pancreatic B-cell. J Biol Chem 1992;267:20713–20720 - PubMed
-
- Rorsman P. The pancreatic beta-cell as a fuel sensor: an electrophysiologist’s viewpoint. Diabetologia 1997;40:487–495 - PubMed
-
- Arredouani A, Guiot Y, Jonas JC, et al. SERCA3 ablation does not impair insulin secretion but suggests distinct roles of different sarcoendoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) pumps for Ca(2+) homeostasis in pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetes 2002;51:3245–3253 - PubMed
-
- Varadi A, Rutter GA. Dynamic imaging of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ concentration in insulin-secreting MIN6 Cells using recombinant targeted cameleons: roles of sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA)-2 and ryanodine receptors. Diabetes 2002;51(Suppl. 1):S190–S201 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

