miR-146a-Mediated extracellular matrix protein production in chronic diabetes complications
- PMID: 21885871
- PMCID: PMC3198068
- DOI: 10.2337/db11-0478
miR-146a-Mediated extracellular matrix protein production in chronic diabetes complications
Abstract
Objective: MicroRNAs (miRNAs), through transcriptional regulation, modulate several cellular processes. In diabetes, increased extracellular matrix protein fibronectin (FN) production is known to occur through histone acetylator p300. Here, we investigated the role of miR-146a, an FN-targeting miRNA, on FN production in diabetes and its relationship with p300.
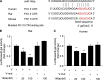
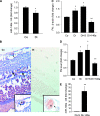
Research design and methods: miR-146a expressions were measured in endothelial cells from large vessels and retinal microvessels in various glucose levels. FN messenger RNA expression and protein levels with or without miR-146a mimic or antagomir transfection were examined. A luciferase assay was performed to detect miR-146a's binding to FN 3'-untranslated region (UTR). Likewise, retinas from type 1 diabetic rats were studied with or without an intravitreal injection of miR-146a mimic. In situ hybridization was used to localize retinal miR-146a. Cardiac and renal tissues were analyzed from type 1 and type 2 diabetic animals.
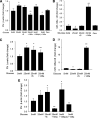
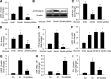
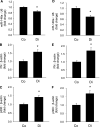
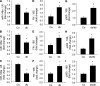
Results: A total of 25 mmol/L glucose decreased miR-146a expression and increased FN expression compared with 5 mmol/L glucose in both cell types. miR-146a mimic transfection prevented such change, whereas miR-146a antagomir transfection in the cells in 5 mmol/L glucose caused FN upregulation. A luciferase assay confirmed miR-146a's binding to FN 3'-UTR. miR-146a was localized in the retinal endothelial cells and was decreased in diabetes. Intravitreal miR-146a mimic injection restored retinal miR-146a and decreased FN in diabetes. Additional experiments showed that p300 regulates miR-146a. Similar changes were seen in the retinas, kidneys, and hearts in type 1 and type 2 diabetic animals.
Conclusions: These studies showed a novel, glucose-induced molecular mechanism in which miR-146a participates in the transcriptional circuitry regulating extracellular matrix protein production in diabetes.
Figures
References
-
- Chen S, Mukherjee S, Chakraborty C, Chakrabarti S. High glucose-induced, endothelin-dependent fibronectin synthesis is mediated via NF-kappa B and AP-1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2003;284:C263–C272 - PubMed
-
- Chen S, Khan ZA, Cukiernik M, Chakrabarti S. Differential activation of NF-kappa B and AP-1 in increased fibronectin synthesis in target organs of diabetic complications. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2003;284:E1089–E1097 - PubMed
-
- Chen S, Feng B, George B, Chakrabarti R, Chen M, Chakrabarti S. Transcriptional coactivator p300 regulates glucose-induced gene expression in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2010;298:E127–E137 - PubMed
-
- Roy S, Cagliero E, Lorenzi M. Fibronectin overexpression in retinal microvessels of patients with diabetes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1996;37:258–266 - PubMed
-
- Xin X, Khan ZA, Chen S, Chakrabarti S. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) in glucose-induced and endothelin-mediated fibronectin synthesis. Lab Invest 2004;84:1451–1459 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

