Acetyl-L-Carnitine Modulates TP53 and IL10 Gene Expression Induced by 3-NPA Evoked Toxicity in PC12 Cells
- PMID: 21886589
- PMCID: PMC3137180
- DOI: 10.2174/157015911795017182
Acetyl-L-Carnitine Modulates TP53 and IL10 Gene Expression Induced by 3-NPA Evoked Toxicity in PC12 Cells
Abstract
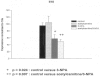
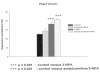
The neurotoxicity induced by the mitochondrial inhibitor 3-nitropropionic acid (3-NPA) is associated with a decrease of ATP synthesis and an increase of free radical production which can lead to apoptosis or necrosis. We have used the PC12, neuron-like rat pheochromocytoma cell line, to study further the mechanism of 3-NPA-evoked neurotoxicity and the effects of acetyl-L-carnitine (ALC) which has neuroprotective actions against various types of mitochondrial inhibitors.Cultured PC 12 cells were exposed to a low dose of 3-NPA 50 (microM) in the presence or absence of 5 mM ALC. The dose of 3-NPA was sub toxic and no changes in pro-apoptotic Bax or anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 gene expression were observed. We followed specific genetic markers to look for changes evoked by 3-NPA toxicity and also changes associated with neuroprotection exerted by the ALC treatment, using RT-PCR arrays (delta-delta method). 3-NPA exposure evoked a decrease in expression of the Tp53 gene. This down regulation was prevented by pretreatment of the cells with ALC. The Tp53 gene responds to cellular stresses and the effects seen here are possibly associated with the 3-NPA evoked changes in mitochondrial metabolism. Other genes associated with stress and apoptosis, Parp-1, Bcl-2, and Bax were not affected by 3-NPA or ALC. The decrease of inflammatory response Il-10 gene expression due to 3-NPA was further lowered by presence of ALC. Other inflammation related genes, Il1rn, Nr3c1 and Cxcr4 were not affected. Interestingly, the glutamate transporter slc17a7, carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase Slc25a20 and heat shock proteins genes, Hsp27, Hmox1 (Hsp32, HO1) as well as Hspa 1a (Hsp 70) increased only when both ALC and small dose of 3-NPA were present. The alterations in gene expression detected in this study suggest role of several intracellular pathways in the neurotoxicity of 3-NPA and the neuroprotection against 3-NPA-induced neurotoxicity by ALC.
Keywords: 3-Nitropropionic acid; Acetyl-L-carnitine; Gene expression; Il10.; Neuroprotection; TP53.
Figures
References
-
- Brouillet E, Jenkins BG, Hyman BT, Ferrante RJ, Kowall NW, Srivastava R, Roy DS, Rosen BR, Beal MF. Age-dependent vulnerability of the striatum to the mitochondrial toxin 3-nitropropionic acid. J. Neurochem. 1993;60:356–359. - PubMed
-
- Nony PA, Scallet AC, Rountree RL, Ye X, Binienda Z. 3-Nitropropionic acid (3-NPA) produces hypothermia and inhibits histochemical labelling of succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) in rat brain. Metab. Brain Dis. 1999;14:83–94. - PubMed
-
- Zeevalk GD, Derr-Yellin E, Nicklas WJ. Relative vulnerability of dopamine and GABA neurons in mesencephalic culture to inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase by malonate and 3-nitropropionic acid and protection by NMDA receptor blockade. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995;275:1124–1130. - PubMed
-
- Virmani A, Gaetani F, Binienda Z, Xu A, Duhart H, Ali SF. Role of mitochondrial dysfunction in neurotoxicity of MPP+: partial protection of PC12 cells by acetyl-L-carnitine. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004;1025:267–273. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous