The homolog of the five SH3-domain protein (HOFI/SH3PXD2B) regulates lamellipodia formation and cell spreading
- PMID: 21886807
- PMCID: PMC3160312
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023653
The homolog of the five SH3-domain protein (HOFI/SH3PXD2B) regulates lamellipodia formation and cell spreading
Abstract
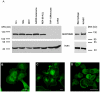
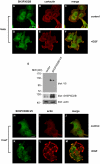
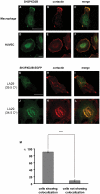
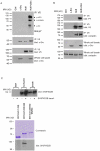
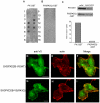
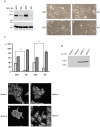
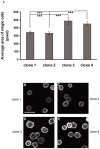
Motility of normal and transformed cells within and across tissues requires specialized subcellular structures, e.g. membrane ruffles, lamellipodia and podosomes, which are generated by dynamic rearrangements of the actin cytoskeleton. Because the formation of these sub-cellular structures is complex and relatively poorly understood, we evaluated the role of the adapter protein SH3PXD2B [HOFI, fad49, Tks4], which plays a role in the development of the eye, skeleton and adipose tissue. Surprisingly, we find that SH3PXD2B is requisite for the development of EGF-induced membrane ruffles and lamellipodia, as well as for efficient cellular attachment and spreading of HeLa cells. Furthermore, SH3PXD2B is present in a complex with the non-receptor protein tyrosine kinase Src, phosphorylated by Src, which is consistent with SH3PXD2B accumulating in Src-induced podosomes. Furthermore, SH3PXD2B closely follows the subcellular relocalization of cortactin to Src-induced podosomes, EGF-induced membrane ruffles and lamellipodia. Because SH3PXD2B also forms a complex with the C-terminal region of cortactin, we propose that SH3PXD2B is a scaffold protein that plays a key role in regulating the actin cytoskeleton via Src and cortactin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Cortactin-CD2-associated protein (CD2AP) complex provides a novel link between epidermal growth factor receptor endocytosis and the actin cytoskeleton.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jun 13;278(24):21805-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211407200. Epub 2003 Apr 2. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12672817
-
CD2AP links cortactin and capping protein at the cell periphery to facilitate formation of lamellipodia.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jan;33(1):38-47. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00734-12. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23090967 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the functional domain requirements of cortactin in invadopodia formation.Eur J Cell Biol. 2007 Apr;86(4):189-206. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2007.01.003. Epub 2007 Mar 6. Eur J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17343955
-
Cortactin branches out: roles in regulating protrusive actin dynamics.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2008 Sep;65(9):687-707. doi: 10.1002/cm.20296. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2008. PMID: 18615630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Understanding TKS4 and TKS5: Molecular Scaffolds Regulating Cellular Processes from Podosome and Invadopodium Formation to Differentiation and Tissue Homeostasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 30;21(21):8117. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218117. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33143131 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Frank-ter Haar syndrome protein Tks4 regulates epidermal growth factor-dependent cell migration.J Biol Chem. 2012 Sep 7;287(37):31321-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.324897. Epub 2012 Jul 24. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22829589 Free PMC article.
-
Large-effect pleiotropic or closely linked QTL segregate within and across ten US cattle breeds.BMC Genomics. 2014 Jun 6;15(1):442. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-442. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24906442 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of the Tks4 Scaffold Protein Induces Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition-Like Changes in Human Colon Cancer Cells.Cells. 2019 Oct 29;8(11):1343. doi: 10.3390/cells8111343. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31671862 Free PMC article.
-
Tks adaptor proteins at a glance.J Cell Sci. 2018 Jan 8;131(1):jcs203661. doi: 10.1242/jcs.203661. J Cell Sci. 2018. PMID: 29311151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of TKS5 in Chromosome Stability and Bladder Cancer Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 18;23(22):14283. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214283. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430759 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pawson T. Dynamic control of signaling by modular adaptor proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007;19:112–116. - PubMed
-
- Ushio-Fukai M. Localizing NADPH oxidase-derived ROS. Sci STKE. 2006. re8 2006. - PubMed
-
- Balla T. Inositol-lipid binding motifs: signal integrators through protein-lipid and protein-protein interactions. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:2093–2104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

