Transduction of SIV-specific TCR genes into rhesus macaque CD8+ T cells conveys the ability to suppress SIV replication
- PMID: 21886812
- PMCID: PMC3160320
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023703
Transduction of SIV-specific TCR genes into rhesus macaque CD8+ T cells conveys the ability to suppress SIV replication
Erratum in
-
Correction: Transduction of SIV-Specific TCR Genes into Rhesus Macaque CD8+ T Cells Conveys the Ability to Suppress SIV Replication.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 28;13(3):e0195246. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195246. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29590210 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: The SIV/rhesus macaque model for HIV/AIDS is a powerful system for examining the contribution of T cells in the control of AIDS viruses. To better our understanding of CD8(+) T-cell control of SIV replication in CD4(+) T cells, we asked whether TCRs isolated from rhesus macaque CD8(+) T-cell clones that exhibited varying abilities to suppress SIV replication could convey their suppressive properties to CD8(+) T cells obtained from an uninfected/unvaccinated animal.
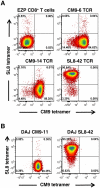
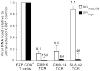
Principal findings: We transferred SIV-specific TCR genes isolated from rhesus macaque CD8(+) T-cell clones with varying abilities to suppress SIV replication in vitro into CD8(+) T cells obtained from an uninfected animal by retroviral transduction. After sorting and expansion, transduced CD8(+) T-cell lines were obtained that specifically bound their cognate SIV tetramer. These cell lines displayed appropriate effector function and specificity, expressing intracellular IFNγ upon peptide stimulation. Importantly, the SIV suppression properties of the transduced cell lines mirrored those of the original TCR donor clones: cell lines expressing TCRs transferred from highly suppressive clones effectively reduced wild-type SIV replication, while expression of a non-suppressing TCR failed to reduce the spread of virus. However, all TCRs were able to suppress the replication of an SIV mutant that did not downregulate MHC-I, recapitulating the properties of their donor clones.
Conclusions: Our results show that antigen-specific SIV suppression can be transferred between allogenic T cells simply by TCR gene transfer. This advance provides a platform for examining the contributions of TCRs versus the intrinsic effector characteristics of T-cell clones in virus suppression. Additionally, this approach can be applied to develop non-human primate models to evaluate adoptive T-cell transfer therapy for AIDS and other diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Rooney CM, Smith CA, Ng CY, Loftin SK, Sixbey JW, et al. Infusion of cytotoxic T cells for the prevention and treatment of Epstein-Barr virus-induced lymphoma in allogeneic transplant recipients. Blood. 1998;92:1549–1555. - PubMed
-
- Walter EA, Greenberg PD, Gilbert MJ, Finch RJ, Watanabe KS, et al. Reconstitution of cellular immunity against cytomegalovirus in recipients of allogeneic bone marrow by transfer of T-cell clones from the donor. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1038–1044. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

