Outcome of closed proximal phalangeal fractures of the hand
- PMID: 21886925
- PMCID: PMC3162680
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5413.83764
Outcome of closed proximal phalangeal fractures of the hand
Abstract
Background: The proximal phalanx (PP) of the fingers is fractured more frequently than the middle or even distal phalanges. The problems of malunion, stiffness and sometimes loss of skin or other soft tissues associated with PP fracture increases the disability. The optimum treatment depends on fracture location, fracture geometry and fracture stability. The objective of the study was to analyse the treatment outcome in a series of closed proximal phalangeal fractures of the hand.
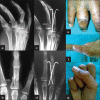
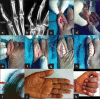
Materials and methods: Eighty-four proximal phalangeal fractures in 68 patients were enrolled from 2007 to 2009. The treatment modalities were broadly categorised into two groups, Group A consisted of conservative treatment, and Group B consisted of surgical treatment. Group A included 47 digits treated with closed reduction (CR) with immobilization (n=43), extension block cast and dynamic traction (n=4), while 37 digits were treated in Group B, which included closed or open reduction (OR) and internal fixation (IF) with K-wires (n=31), OR and IF with stainless-steel wiring (n=2), and mini external-fixator (n=4). Belsky's criteria and Gingrass' criteria were used for assessment of finger injuries and to assess the efficacy of conservative and surgical modalities for closed proximal phalangeal fractures of the hand.
Results: Average period of follow-up was 1 year (range 10-14 months). The excellent to good results seen in Groups A and B were 89% and 92%, respectively. Six complications were seen in Group A, which included four cases with malunion and two cases with digital stiffness. Three complications were seen in Group B, which included one each of malunion, digital stiffness and extensor lag. Overall, maximum poor results (n=4) were seen with CR and buddy strapping.
Conclusion: Conservative treatment is an inexpensive method, particularly suitable for stable fractures, and in patients who are poor candidates for surgery, Surgical modalities have distinct advantage of stable fixation, but with added risk of digital stiffness. Percutaneous pinning is a reliable, most commonly used surgical modality and technically easier. Both conservative and surgical modalities have good efficacy when used judiciously.
Keywords: Proximal phalanx fracture; closed reduction; hand; open reduction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Management of phalangeal fractures of hand.J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2006 Oct-Dec;18(4):38-41. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2006. PMID: 17591008
-
Management of Unstable Phalangeal Shaft Fractures Using External Minifixator.Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2019 Jun 30;21(3):181-185. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0013.2922. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2019. PMID: 32015198
-
Conservative management of difficult phalangeal fractures.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987 Jan;(214):23-30. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987. PMID: 3791748
-
Percutaneous pinning for treating distal radial fractures in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Feb 7;2(2):CD006080. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006080.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32032439 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of extra-articular proximal and middle phalangeal fractures of the hand: a systematic review.Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2017 Aug;12(2):63-76. doi: 10.1007/s11751-017-0279-5. Epub 2017 Mar 4. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2017. PMID: 28260179 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Safe corridors for K-wiring in phalangeal fractures.Indian J Orthop. 2015 Jul-Aug;49(4):388-92. doi: 10.4103/0019-5413.159591. Indian J Orthop. 2015. PMID: 26229157 Free PMC article.
-
Dorsal Cortical Alignment Predicts Functional Outcomes in Proximal Phalangeal Fractures Treated with Intramedullary Headless Compression Screws but Not in Metacarpal Fractures.J Clin Med. 2025 Jul 2;14(13):4691. doi: 10.3390/jcm14134691. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40649064 Free PMC article.
-
Principles of hand fracture management.Open Orthop J. 2012;6:43-53. doi: 10.2174/1874325001206010043. Epub 2012 Feb 23. Open Orthop J. 2012. PMID: 22423303 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of Conservatively Managed Isolated Extra-Articular Proximal Phalanx Finger Fractures in Adults.JPRAS Open. 2024 May 9;41:37-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jpra.2024.05.002. eCollection 2024 Sep. JPRAS Open. 2024. PMID: 38872867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Needle Cap External Fixator for Proximal Phalanx Fracture - A Case Report.J Orthop Case Rep. 2022 Oct;12(10):107-109. doi: 10.13107/jocr.2022.v12.i10.3388. J Orthop Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 36874891 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stern PJ. Factures of metacarpals and phalanges. In: Green DP, Hotchkiss RN, Pederson WC, editors. Green's operative hand surgery. 4th ed. Vol. 1. Philadelphia, US: Churchill Livingstone; 1999. pp. 711–57.
-
- Watson-Jones R, Barton NJ. Fractures and Joint Injuries of the hand. In: Wilson JN, editor. Watson-Jones fractures and joint Injuries. 7th ed. Noida: Elsevier Publishers; 2009. pp. 650–95.
-
- Barton N. Internal fixation of the hand. J Hand Surg Br. 1989;14:139–42. - PubMed
-
- Margic K. External fixation of closed metacarpal and phalangeal fractures of digits: A prospective study of one hundred consecutive patients. J Hand Surg Br. 2006;31:30–40. - PubMed
-
- Burkhalter WE. Closed treatment of hand fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 1989;14:390–3. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
