Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor
- PMID: 21887011
- PMCID: PMC3162870
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-029X.57679
Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor
Abstract
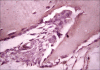
Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor (DGCT) is a rare tumorous form of calcifying odontogenic cyst and only a small number of cases have been described. It is a locally invasive neoplasm that is characterized by ameloblastoma-like epithelial islands, ghost cells and dentinoid. The present report describes a case of a 21-year-old male with a tumor in the posterior region of the mandible, showing features of DGCT.
Keywords: Dentinoid; dentinogenic ghost cell tumor; ghost cell.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







References
-
- Tajima Y, Ohno J, Ustumi N. The dentinogenic ghost cell tumor. J Oral Pathol. 1986;15:359–62. - PubMed
-
- Gunhan O, Mocan A, Can C, Kisnisci R, Aksu AY, Finci R. Epithelial odontogenic ghost cell tumor: report of a peripheral solid variant and review of the literature. Ann Dent. 1991;50:8–11. - PubMed
-
- Toida M. So-called calcifying odontogenic cyst: review and discussion on the terminology and classification. J Oral Pathol Med. 1998;27:49–52. - PubMed
-
- Praetorius F, Ledesma-Montes C. Dentinogenic ghost cell tumour. In: Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart P, Sidransky D, editors. Pathology and genetics of head and neck tumours. World Health Organization classification of tumours. Lyon, France: IARC press; 2005. p. 314.
-
- Gunhan O, Sengun O, Celasun B. Epithelial odontogenic ghost cell tumor: report of a case. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1989;47:864–7. - PubMed

