CK2 phosphorylation of Schistosoma mansoni HMGB1 protein regulates its cellular traffic and secretion but not its DNA transactions
- PMID: 21887276
- PMCID: PMC3160966
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023572
CK2 phosphorylation of Schistosoma mansoni HMGB1 protein regulates its cellular traffic and secretion but not its DNA transactions
Abstract
Background: The helminth Schistosoma mansoni parasite resides in mesenteric veins where fecundated female worms lay hundred of eggs daily. Some of the egg antigens are trapped in the liver and induce a vigorous granulomatous response. High Mobility Group Box 1 (HMGB1), a nuclear factor, can also be secreted and act as a cytokine. Schistosome HMGB1 (SmHMGB1) is secreted by the eggs and stimulate the production of key cytokines involved in the pathology of schistosomiasis. Thus, understanding the mechanism of SmHMGB1 release becomes mandatory. Here, we addressed the question of how the nuclear SmHMGB1 can reach the extracellular space.
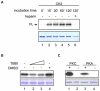
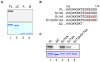
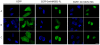
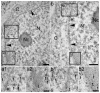
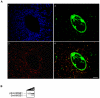
Principal findings: We showed in vitro and in vivo that CK2 phosphorylation was involved in the nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of SmHMGB1. By site-directed mutagenesis we mapped the two serine residues of SmHMGB1 that were phosphorylated by CK2. By DNA bending and supercoiling assays we showed that CK2 phosphorylation of SmHMGB1 had no effect in the DNA binding activities of the protein. We showed by electron microscopy, as well as by cell transfection and fluorescence microscopy that SmHMGB1 was present in the nucleus and cytoplasm of adult schistosomes and mammalian cells. In addition, we showed that treatments of the cells with either a phosphatase or a CK2 inhibitor were able to enhance or block, respectively, the cellular traffic of SmHMGB1. Importantly, we showed by confocal microscopy and biochemically that SmHMGB1 is significantly secreted by S. mansoni eggs of infected animals and that SmHMGB1 that were localized in the periovular schistosomotic granuloma were phosphorylated.
Conclusions: We showed that secretion of SmHMGB1 is regulated by phosphorylation. Moreover, our results suggest that egg-secreted SmHMGB1 may represent a new egg antigen. Therefore, the identification of drugs that specifically target phosphorylation of SmHMGB1 might block its secretion and interfere with the pathogenesis of schistosomiasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- WHO. TDR Strategic Direction for Research. Schistosomiasis World Health Organization. Geneve; 2002.
-
- Oliveira VR, El-Cheikh MC, Aguiar AM, Balduino A, de Fatima BPM, et al. Schistosoma mansoni egg-induced hepatic granulomas in mice deficient for the interferon-gamma receptor have altered populations of macrophages, lymphocytes and connective tissue cells. Microbes Infect. 2000;2:1817–1826. - PubMed
-
- Boros DL. Immunoregulation of granuloma formation in murine schistosomiasis mansoni. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;465:313–323. - PubMed
-
- Caldas IR, Campi-Azevedo AC, Oliveira LF, Silveira AM, Oliveira RC, et al. Human schistosomiasis mansoni: immune responses during acute and chronic phases of the infection. Acta Trop. 2008;108:109–117. - PubMed
-
- Stros M. HMGB proteins: interactions with DNA and chromatin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1799:101–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

