IL-33 synergizes with TCR and IL-12 signaling to promote the effector function of CD8+ T cells
- PMID: 21887788
- PMCID: PMC3332117
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.201141629
IL-33 synergizes with TCR and IL-12 signaling to promote the effector function of CD8+ T cells
Abstract
The effector functions of CD8(+) T cells are influenced by tissue inflammatory microenvironments. IL-33, a member of the IL-1 family, acts as a danger signal after its release during cell necrosis. The IL-33/ST2 axis has been implicated in various Th2 responses. Its role in CD8(+) T-cell-mediated immune response is, however, not known. Here we find that type 1 cytotoxic T (Tc1) cells cultured in vitro unexpectedly express high levels of the IL-33 receptor ST2. Interestingly, the expression of ST2 in Tc1 cells is dependent on T-bet, a master Th1/Tc1 transcription factor. In addition, IL-33 enhances TCR-triggered IFN-γ production. IL-33 together with IL-12 can stimulate IFN-γ production in Tc1 cells. Moreover, IL-33 synergizes with IL-12 to promote CD8(+) T-cell effector function. The synergistic effect of IL-33 and IL-12 is partly mediated by Gadd45b. Together, these in vitro data establish a novel role of IL-33 in promoting effector type 1 adaptive immune responses.
Copyright © 2011 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
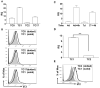
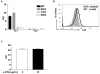
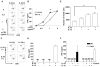
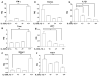
Similar articles
-
Pretreatment of activated human CD8 T cells with IL-12 leads to enhanced TCR-induced signaling and cytokine production.Mol Immunol. 2017 Jan;81:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2016.11.008. Epub 2016 Nov 22. Mol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27883938 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-21 and cellular activation concurrently induce potent cytotoxic function and promote antiviral activity in human CD8 T cells.Hum Immunol. 2011 Feb;72(2):115-23. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2010.10.015. Epub 2010 Oct 25. Hum Immunol. 2011. PMID: 20977918 Free PMC article.
-
CD8-mediated type 1 antitumor responses selectively modulate endogenous differentiated and nondifferentiated T cell localization, activation, and function in progressive breast cancer.J Immunol. 2006 Dec 1;177(11):8191-201. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.11.8191. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17114496
-
IL-33/ST2 axis in inflammation and immunopathology.Immunol Res. 2012 Apr;52(1-2):89-99. doi: 10.1007/s12026-012-8283-9. Immunol Res. 2012. PMID: 22392053 Review.
-
IL-33 family members and asthma - bridging innate and adaptive immune responses.Curr Opin Immunol. 2010 Dec;22(6):800-6. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2010.10.006. Epub 2010 Nov 9. Curr Opin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 21071194 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pulmonary resident memory T cells in respiratory virus infection and their inspiration on therapeutic strategies.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 12;13:943331. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.943331. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36032142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alarmin' Immunologists: IL-33 as a Putative Target for Modulating T Cell-Dependent Responses.Front Immunol. 2015 Jun 2;6:232. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00232. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26082774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Pro-tumorigenic IL-33 Involved in Antitumor Immunity: A Yin and Yang Cytokine.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 26;9:2506. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02506. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30416507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-33, an Alarmin of the IL-1 Family Involved in Allergic and Non Allergic Inflammation: Focus on the Mechanisms of Regulation of Its Activity.Cells. 2021 Dec 30;11(1):107. doi: 10.3390/cells11010107. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alarmin IL-33 acts as an immunoadjuvant to enhance antigen-specific tumor immunity.Cancer Res. 2014 Mar 15;74(6):1789-800. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-2729. Epub 2014 Jan 21. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24448242 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liew FY, Pitman NI, McInnes IB. Disease-associated functions of IL-33: the new kid in the IL-1 family. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:103–110. - PubMed
-
- Dinarello CA. Immunological and inflammatory functions of the interleukin-1 family. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:519–550. - PubMed
-
- Luthi AU, Cullen SP, McNeela EA, Duriez PJ, Afonina IS, Sheridan C, Brumatti G, et al. Suppression of interleukin-33 bioactivity through proteolysis by apoptotic caspases. Immunity. 2009;31:84–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

