Management of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) and smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM)
- PMID: 21888255
- PMCID: PMC3923465
Management of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) and smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM)
Abstract
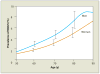
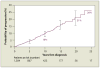
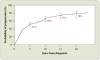
Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) is defined as a serum M protein level of less than 3 g/dL, less than 10% clonal plasma cells in the bone marrow, and the absence of end-organ damage. The prevalence of MGUS is 3.2% in the white population but is approximately twice that high in the black population. MGUS may progress to multiple myeloma, AL amyloidosis, Waldenström macroglobulinemia, or lymphoma. The risk of progression is approximately 1% per year, but the risk continues even after more than 25 years of observation. Risk factors for progression include the size of the serum M protein, the type of serum M protein, the number of plasma cells in the bone marrow, and the serum free light chain ratio. Smoldering (asymptomatic) multiple myeloma (SMM) is characterized by the presence of an M protein level of 3 g/dL or higher and/or 10% or more monoclonal plasma cells in the bone marrow but no evidence of end-organ damage. The overall risk of progression to a malignant condition is 10% per year for the first 5 years, approximately 3% per year for the next 5 years, and 1% to 2% per year for the following 10 years. Patients with both MGUS and SMM must be followed up for their lifetime.
Figures

Comment in
-
Multiple myeloma precursor disease: current clinical and epidemiological insights and future opportunities.Oncology (Williston Park). 2011 Jun;25(7):589-90. Oncology (Williston Park). 2011. PMID: 21888256 Review. No abstract available.
-
MGUS and smoldering myeloma: the most prevalent of plasma cell dyscrasias.Oncology (Williston Park). 2011 Jun;25(7):594, 596. Oncology (Williston Park). 2011. PMID: 21888257 Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kyle RA. Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance: natural history in 241 cases. Am J Med. 1978;64:814–26. - PubMed
-
- Criteria for the classification of monoclonal gammopathies, multiple myeloma and related disorders: a report of the International Myeloma Working Group. Br J Haematol. 2003;121:749–57. - PubMed
-
- Katzmann JA, Dispenzieri A, Kyle RA, et al. Elimination of the need for urine studies in the screening algorithm for monoclonal gammopathies by using serum immunofixation and free light chain assays. Mayo Clin Proc. 2006;81:1575–8. - PubMed
-
- Berenson JR, Anderson KC, Audell RA, et al. Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance: a consensus statement. Br J Haematol. 2010;150:28–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

