DNA double-strand break induction in Ku80-deficient CHO cells following boron neutron capture reaction
- PMID: 21888676
- PMCID: PMC3179943
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-6-106
DNA double-strand break induction in Ku80-deficient CHO cells following boron neutron capture reaction
Abstract
Background: Boron neutron capture reaction (BNCR) is based on irradiation of tumors after accumulation of boron compound. 10B captures neutrons and produces an alpha (4He) particle and a recoiled lithium nucleus (7Li). These particles have the characteristics of high linear energy transfer (LET) radiation and have marked biological effects. The purpose of this study is to verify that BNCR will increase cell killing and slow disappearance of repair protein-related foci to a greater extent in DNA repair-deficient cells than in wild-type cells.
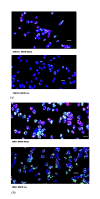
Methods: Chinese hamster ovary (CHO-K1) cells and a DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair deficient mutant derivative, xrs-5 (Ku80 deficient CHO mutant cells), were irradiated by thermal neutrons. The quantity of DNA-DSBs following BNCR was evaluated by measuring the phosphorylation of histone protein H2AX (gamma-H2AX) and 53BP1 foci using immunofluorescence intensity.
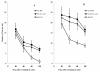
Results: Two hours after neutron irradiation, the number of gamma-H2AX and 53BP1 foci in the CHO-K1 cells was decreased to 36.5-42.8% of the levels seen 30 min after irradiation. In contrast, two hours after irradiation, foci levels in the xrs-5 cells were 58.4-69.5% of those observed 30 min after irradiation. The number of gamma-H2AX foci in xrs-5 cells at 60-120 min after BNCT correlated with the cell killing effect of BNCR. However, in CHO-K1 cells, the RBE (relative biological effectiveness) estimated by the number of foci following BNCR was increased depending on the repair time and was not always correlated with the RBE of cytotoxicity.
Conclusion: Mutant xrs-5 cells show extreme sensitivity to ionizing radiation, because xrs-5 cells lack functional Ku-protein. Our results suggest that the DNA-DSBs induced by BNCR were not well repaired in the Ku80 deficient cells. The RBE following BNCR of radio-sensitive mutant cells was not increased but was lower than that of radio-resistant cells. These results suggest that gamma-ray resistant cells have an advantage over gamma-ray sensitive cells in BNCR.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Relative biological effects of neutron mixed-beam irradiation for boron neutron capture therapy on cell survival and DNA double-strand breaks in cultured mammalian cells.J Radiat Res. 2013 Jan;54(1):70-5. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrs079. Epub 2012 Sep 10. J Radiat Res. 2013. PMID: 22966174 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-rate effect was observed in T98G glioma cells following BNCT.Appl Radiat Isot. 2014 Jun;88:81-5. doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2013.11.117. Epub 2013 Dec 10. Appl Radiat Isot. 2014. PMID: 24360864
-
DNA Double-strand Breaks Induced byFractionated Neutron Beam Irradiation for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy.Anticancer Res. 2017 Apr;37(4):1681-1685. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.11499. Anticancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28373429
-
DNA damage and biological responses induced by Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT).Enzymes. 2022;51:65-78. doi: 10.1016/bs.enz.2022.08.005. Epub 2022 Sep 27. Enzymes. 2022. PMID: 36336409 Review.
-
DNA Damage Response and Repair in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jan 2;14(1):127. doi: 10.3390/genes14010127. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672868 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Boron Neutron Capture Therapy Eliminates Radioresistant Liver Cancer Cells by Targeting DNA Damage and Repair Responses.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2022 Dec 29;9:1385-1401. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S383959. eCollection 2022. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2022. PMID: 36600987 Free PMC article.
-
DNA strand breaks based on Monte Carlo simulation in and around the Lipiodol with flattening filter and flattening filter-free photon beams.Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2022 Jul 29;27(3):392-400. doi: 10.5603/RPOR.a2022.0067. eCollection 2022. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2022. PMID: 36186706 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting aberrant DNA double-strand break repair in triple-negative breast cancer with alpha-particle emitter radiolabeled anti-EGFR antibody.Mol Cancer Ther. 2013 Oct;12(10):2043-54. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0108. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013. PMID: 23873849 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Specific Cellular DNA Damage Response and Repair Induced by the Mixed Radiation Field During Boron Neutron Capture Therapy.Front Oncol. 2021 May 19;11:676575. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.676575. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34094980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Model for Estimating Dose-Rate Effects on Cell-Killing of Human Melanoma after Boron Neutron Capture Therapy.Cells. 2020 Apr 30;9(5):1117. doi: 10.3390/cells9051117. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32365916 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jeggo PA, Kemp LM. X-ray-sensitive mutants of Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Isolation and cross sensitivity to other DNA-damaging agents. Mutat Res. 1983;112:313–327. - PubMed
-
- Kemp LM, Sedgwick SG, Jeggo PA. X-ray sensitive mutants of Chinese hamster ovary cells defective in double-strand break rejoining. Mutat Res. 1984;132:189–196. - PubMed
-
- Ritter S, Durante M. Heavy-ion induced chromosal aberrations: A review. Mutat Res. 2010;701:38–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

