Expert opinion: Responsive polymer nanoparticles in cancer therapy
- PMID: 21888972
- PMCID: PMC3269567
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2011.08.004
Expert opinion: Responsive polymer nanoparticles in cancer therapy
Abstract
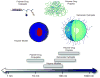
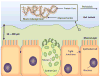
Polymeric nanoparticles are emerging as an attractive treatment options for cancer due to their favorable size distribution, drug carrying capacity, and tunable properties. In particular, intelligent nanoparticles that respond to biological cues are of interest because of their ability to provide controlled release at a specific site. Tumor sites display abnormal pH profiles and pathophysiology that can be exploited to provide localized release. In this expert opinion, we discuss passive and active targeting of nanoparticles and several classes of pH-responsive nanoparticles.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fabrication Of Dual pH/redox-Responsive Lipid-Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles For Anticancer Drug Delivery And Controlled Release.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Oct 3;14:8001-8011. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S226798. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31632014 Free PMC article.
-
Classification of stimuli-responsive polymers as anticancer drug delivery systems.Drug Deliv. 2015 Feb;22(2):145-55. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2014.887157. Epub 2014 Feb 19. Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 24547737 Review.
-
Visible Light and pH Responsive Polymer-Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanohybrids for Controlled Release.Macromol Biosci. 2016 Jul;16(7):990-4. doi: 10.1002/mabi.201600008. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Macromol Biosci. 2016. PMID: 26938147
-
[Advances in the study of tumor pH-responsive polymeric micelles for cancer drug targeting delivery].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2009 Dec;44(12):1328-35. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2009. PMID: 21351464 Review. Chinese.
-
Superparamagnetic Reduction/pH/Temperature Multistimuli-Responsive Nanoparticles for Targeted and Controlled Antitumor Drug Delivery.Mol Pharm. 2015 Dec 7;12(12):4188-99. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00342. Epub 2015 Nov 20. Mol Pharm. 2015. PMID: 26554495
Cited by
-
Preparation, characterization and application of star-shaped PCL/PEG micelles for the delivery of doxorubicin in the treatment of colon cancer.Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:971-82. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S39532. Epub 2013 Mar 8. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013. PMID: 23493403 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient ultrasound-mediated drug delivery to orthotopic liver tumors - Direct comparison of doxorubicin-loaded nanobubbles and microbubbles.J Control Release. 2024 Mar;367:135-147. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.01.028. Epub 2024 Jan 25. J Control Release. 2024. PMID: 38237687 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing Microfluidic Channel Design with Tilted Rectangular Baffles for Enhanced mRNA-Lipid Nanoparticle Preparation.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2025 Jun 9;11(6):3762-3772. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.4c02373. Epub 2025 May 21. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2025. PMID: 40396945 Free PMC article.
-
Co-delivery of siRNA and therapeutic agents using nanocarriers to overcome cancer resistance.Nano Today. 2012 Aug 1;7(4):367-379. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2012.06.013. Nano Today. 2012. PMID: 26257819 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and Evaluation of Diosmin-Loaded Diphenylcarbonate-Cross-Linked Cyclodextrin Nanosponges for Breast Cancer Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Dec 23;16(1):19. doi: 10.3390/ph16010019. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36678517 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dincer S, Turk M, Piskin E. Intelligent polymers as nonviral vectors. Gene Ther. 2005;12:S139–S145. - PubMed
-
- Couvreur P, Brigger I, Dubernet C. Nanoparticles in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 2002;54:631–651. - PubMed
-
- Langer R, Peppas NA. Advances in biomaterials, drug delivery, and bionanotechnology. AIChE J. 2003;49:2990–3006.
-
- Couvreur P, Puisieux F. Nanoparticles and Microparticles for the Delivery of Polypeptides and Proteins. Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 1993;10:141–162.
-
- Couvreur P, Dubernet C, Puisieux F. Controlled Drug-Delivery with Nanoparticles -Current Possibilities and Future-Trends. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 1995;41:2–13.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

