Expert opinion: Responsive polymer nanoparticles in cancer therapy
- PMID: 21888972
- PMCID: PMC3269567
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2011.08.004
Expert opinion: Responsive polymer nanoparticles in cancer therapy
Abstract
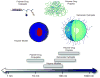
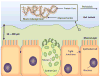
Polymeric nanoparticles are emerging as an attractive treatment options for cancer due to their favorable size distribution, drug carrying capacity, and tunable properties. In particular, intelligent nanoparticles that respond to biological cues are of interest because of their ability to provide controlled release at a specific site. Tumor sites display abnormal pH profiles and pathophysiology that can be exploited to provide localized release. In this expert opinion, we discuss passive and active targeting of nanoparticles and several classes of pH-responsive nanoparticles.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Dincer S, Turk M, Piskin E. Intelligent polymers as nonviral vectors. Gene Ther. 2005;12:S139–S145. - PubMed
-
- Couvreur P, Brigger I, Dubernet C. Nanoparticles in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 2002;54:631–651. - PubMed
-
- Langer R, Peppas NA. Advances in biomaterials, drug delivery, and bionanotechnology. AIChE J. 2003;49:2990–3006.
-
- Couvreur P, Puisieux F. Nanoparticles and Microparticles for the Delivery of Polypeptides and Proteins. Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 1993;10:141–162.
-
- Couvreur P, Dubernet C, Puisieux F. Controlled Drug-Delivery with Nanoparticles -Current Possibilities and Future-Trends. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 1995;41:2–13.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

