RT-SVR+q: a strategy for post-Mascot analysis using retention time and q value metric to improve peptide and protein identifications
- PMID: 21888997
- PMCID: PMC3225640
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jprot.2011.08.013
RT-SVR+q: a strategy for post-Mascot analysis using retention time and q value metric to improve peptide and protein identifications
Abstract
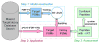
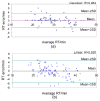
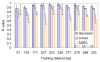
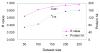
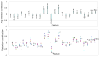
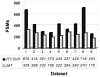
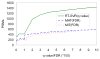
Shotgun proteomics commonly utilizes database search like Mascot to identify proteins from tandem MS/MS spectra. False discovery rate (FDR) is often used to assess the confidence of peptide identifications. However, a widely accepted FDR of 1% sacrifices the sensitivity of peptide identification while improving the accuracy. This article details a machine learning approach combining retention time based support vector regressor (RT-SVR) with q value based statistical analysis to improve peptide and protein identifications with high sensitivity and accuracy. The use of confident peptide identifications as training examples and careful feature selection ensures high R values (>0.900) for all models. The application of RT-SVR model on Mascot results (p=0.10) increases the sensitivity of peptide identifications. q Value, as a function of deviation between predicted and experimental RTs (ΔRT), is used to assess the significance of peptide identifications. We demonstrate that the peptide and protein identifications increase by up to 89.4% and 83.5%, respectively, for a specified q value of 0.01 when applying the method to proteomic analysis of the natural killer leukemia cell line (NKL). This study establishes an effective methodology and provides a platform for profiling confident proteomes in more relevant species as well as a future investigation of accurate protein quantification.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Enhanced peptide identification by electron transfer dissociation using an improved Mascot Percolator.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Aug;11(8):478-91. doi: 10.1074/mcp.O111.014522. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22493177 Free PMC article.
-
A peptide-retrieval strategy enables significant improvement of quantitative performance without compromising confidence of identification.J Proteomics. 2017 Jan 30;152:276-282. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2016.11.020. Epub 2016 Nov 27. J Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 27903464
-
[A new peptide retention time prediction method for mass spectrometry based proteomic analysis by a serial and parallel support vector machine model].Se Pu. 2012 Sep;30(9):857-63. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1123.2012.06021. Se Pu. 2012. PMID: 23285964 Chinese.
-
Current algorithmic solutions for peptide-based proteomics data generation and identification.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2013 Feb;24(1):31-8. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2012.10.013. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23142544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein identification by tandem mass spectrometry and sequence database searching.Methods Mol Biol. 2007;367:87-119. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-275-0:87. Methods Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17185772 Review.
References
-
- Hunt DF, Michel H, Dickinson TA, Shabanowitz J, Cox AL, Sakaguchi K, et al. Peptides presented to the immune system by the murine class II major histocompatibility complex molecule I-Ad. Science. 1992;256:1817–20. - PubMed
-
- Wolters DA, Washburn MP, Yates JR., 3rd An automated multidimensional protein identification technology for shotgun proteomics. Anal Chem. 2001;73:5683–90. - PubMed
-
- Foster LJ, de Hoog CL, Zhang Y, Xie X, Mootha VK, Mann M. A mammalian organelle map by protein correlation profiling. Cell. 2006;125:187–99. - PubMed
-
- Eng JK, Mccormack AL, Yates JR. An Approach to Correlate Tandem Mass-Spectral Data of Peptides with Amino-Acid-Sequences in a Protein Database. J Am Soc Mass Spectr. 1994;5:976–89. - PubMed
-
- Perkins DN, Pappin DJ, Creasy DM, Cottrell JS. Probability-based protein identification by searching sequence databases using mass spectrometry data. Electrophoresis. 1999;20:3551–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

