FKBP51 and FKBP52 in signaling and disease
- PMID: 21889356
- PMCID: PMC3229651
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2011.08.001
FKBP51 and FKBP52 in signaling and disease
Abstract
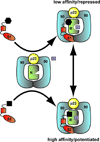
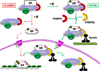
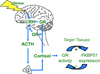
FKBP51 and FKBP52 are diverse regulators of steroid hormone receptor signaling, including receptor maturation, hormone binding and nuclear translocation. Although structurally similar, they are functionally divergent, which is largely attributed to differences in the FK1 domain and the proline-rich loop. FKBP51 and FKBP52 have emerged as likely contributors to a variety of hormone-dependent diseases, including stress-related diseases, immune function, reproductive functions and a variety of cancers. In addition, recent studies have implicated FKBP51 and FKBP52 in Alzheimer's disease and other protein aggregation disorders. This review summarizes our current understanding of FKBP51 and FKBP52 interactions within the receptor-chaperone complex, their contributions to health and disease, and their potential as therapeutic targets for the treatment of these diseases.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
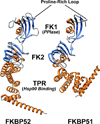
References
-
- Sanchez ER. Hsp56: a novel heat shock protein associated with untransformed steroid receptor complexes. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:22067–22070. - PubMed
-
- Smith DF, et al. Purification of unactivated progesterone receptor and identification of novel receptor-associated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:3996–4003. - PubMed
-
- Pirkl F, Buchner J. Functional analysis of the Hsp90-associated human peptidyl prolyl cis/trans isomerases FKBP51, FKBP52 and Cyp40. J Mol Biol. 2001;308:795–806. - PubMed
-
- Cheung-Flynn J, Place, Sean P, Cox, Marc B, Prapapanich V, Smith, David F. 12 FKBP Co-Chaperone in Steroid Receptor Complexes. In: Calderwood SK, editor. Cell Stress Proteins. Springer: 2007. pp. 275–306.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

